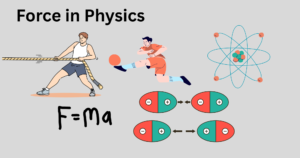
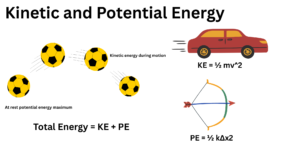
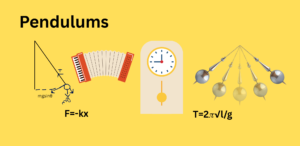
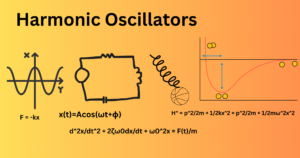
Force: Simple Concept and Types Explained
What is Force in Physics According to the theories, force came into existence just after the Big-Bang. Since then, force has remained as the most studied concept in physics. Physics came into action after the discovery of force and found … Read more