Sulfur Cycle: Definition, Steps, Processes, Importance
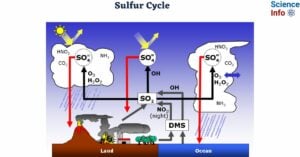
The sulfur cycle is a biogeochemical process in which sulfur circulates around the Earth’s atmosphere, soil, water, and living organisms. Sulfur is the fifth most prevalent element in the universe, … Read more