Upthrust: Principle, Concept, Measurement, Applications, Examples
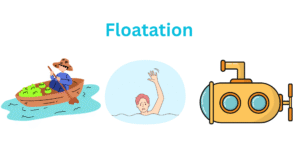
What is Upthrust? All liquids acquire force on the immersing or submerging bodies on it. This goes slightly against the gravity. Tise pushing force of the liquid increases even vigorously on going deeper down and generates a pressure on the … Read more