Feather and Coin Experiment: Principle, Examples, Implications
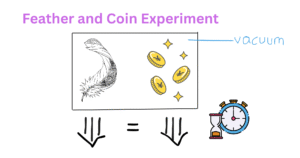
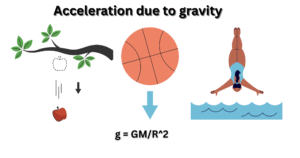
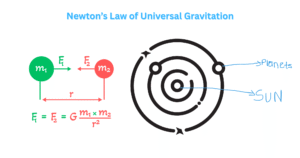
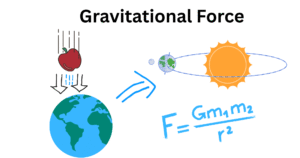
Introduction to the Feather and Coin Experiment When gravity was not defined, everything was suspected to fall depending on its mass. According to Aristotle, massive objects fall more rapidly than the tiny ones. On studying this concept, Galileo Galilei had … Read more