Interesting Science Videos
Atomic Mass Definition
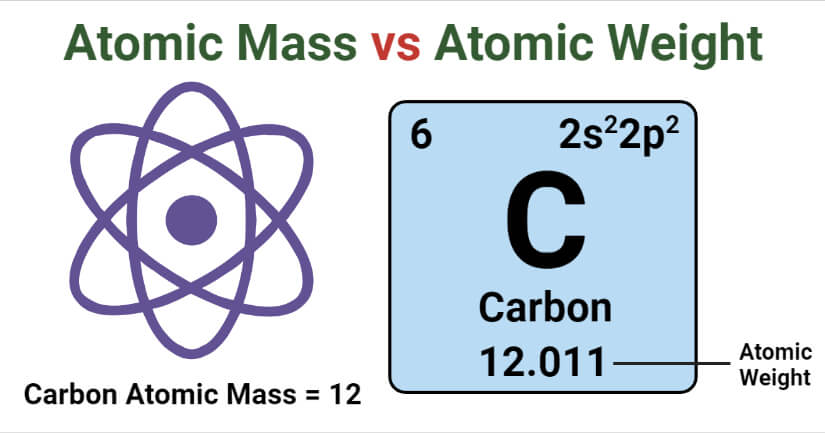
Atomic mass is the mass of an atom or an isotope which includes the total mass of the nucleus and the electrons present in the periphery.
- Most of the contribution is made by the nucleus as it contains the heavier subatomic particles, while lesser contributions are made by the electrons and nuclear binding energy.
- The SI unit of atomic mass is the kilogram (kg), but it is often expressed in terms of non-SI unit, Dalton. 1 Dalton is defined as the 1/12th of the mass of a single carbon-12 atom.
- The atomic mass of a chemical species is often slightly less than the sum of the masses of protons, neutrons, and electrons due to the loss of some energy due to binding energy mass loss.
- Atomic mass represents the mass of an atom which can only be one isotope. This allows precise measurement of different atoms in contrast to the abundance-weighted average, like in relative atomic weight.
- Atomic mass can also be used for the determination of molecular mass, which differs slightly in numerical value from the molar mass.
Read Also: Atom vs Molecule- Definition, 12 Major Differences, Examples
Atomic Weight Definition
Atomic weight, also called relative atomic mass, is the weighted arithmetic mean of the relative isotopic mass of all the isotopes of a particular element depending on the abundance of each of those isotopes.
- Besides, atomic weight can also be related to the sum of the total number of protons and neutrons present in an atom.
- The value of atomic weight might be slightly different than the atomic mass as a substance contains different isotopes that have different atomic or isotopic mass.
- Atomic weights are expressed in terms of atomic mass units (AMU), which are also called daltons.
- Atomic weight is fundamental to chemistry as the most chemical reaction takes place via numerical relationships between atoms.
- Since the determination of the number of atoms involved in a reaction is quite difficult, most calculations are made by measuring the reactants and products to obtain information through atomic weight.
- Atomic weight is more common as it is more convenient and results in consistency throughout different regions of the world.
7 Key Differences (Atomic Mass vs Atomic Weight)
| Characteristics | Atomic mass | Atomic weight |
| Definition | Atomic mass is the mass of an atom or an isotope which includes the total mass of the nucleus and the electrons present in the periphery. | Atomic weight, also called relative atomic mass, is the weighted arithmetic mean of the relative isotopic mass of all the isotopes of a particular element depending on the abundance of each of those isotopes. |
| Calculation | Atomic mass is calculated by measuring the masses of protons, neutrons, and electrons of the atom. | Atomic weight is calculated by determining the percentage abundance of all the isotopes of a chemical element. |
| Isotopes | Atomic mass doesn’t depend on the isotopic mass of different isotopes of an element. | Atomic weight depends on the isotopic mass of different isotopes of an element. |
| Prevalent | Atomic mass is less prevalent than atomic weight. | Atomic weight is more prevalent in chemistry due to its use in the calculation of different chemical quantities involved in reactions. |
| Molecules | The sum of the atomic masses of all the atoms present in a molecule gives the molecular mass. | The sum of the atomic weights of all the atoms present in a molecule gives the molecular weight. |
| SI unit | The SI unit of atomic mass is the kilogram, but the non-SI unit, AMU, is often used. | The SI unit of atomic weight is AMU or daltons. |
| Value | The value of atomic mass is usually a whole number. | The value of atomic weight may or may not be a whole number. |
Atomic Mass vs. Atomic Weight (Video By MedSchoolCoach)
References and Sources
- 4% – https://www.calculatoratoz.com/en/atomic-mass-calculator/node-342?FormulaId=309
- 3% – https://www.britannica.com/science/atomic-weight
- 2% – https://www.thoughtco.com/atomic-weight-and-atomic-mass-difference-4046144
- 2% – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Atomic_mass
- 1% – https://www.thoughtco.com/how-to-calculate-atomic-mass-603823
- 1% – https://www.onlinemathlearning.com/relative-atomic-mass.html
- 1% – https://www.minichemistry.com/atomic-mass-molecular-mass.html
- 1% – https://www.differencebetween.com/difference-between-atomic-mass-unit-and-vs-atomic-mass/
- 1% – https://quizlet.com/7200704/chemistry-4-flash-cards/
- 1% – https://physics.stackexchange.com/questions/332972/why-was-carbon-12-chosen-for-the-atomic-mass-unit
- 1% – https://pages.mtu.edu/~pcharles/SCIHISTORY/Atomic_weight_.html
- 1% – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Standard_atomic_weight
- 1% – http://dictionary.sensagent.com/Molecular%20mass/en-en/
- <1% – https://www.thoughtco.com/experimental-determination-of-avogadros-number-602107
