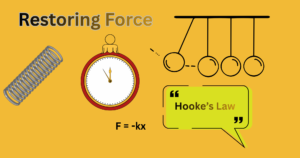
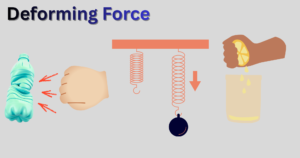
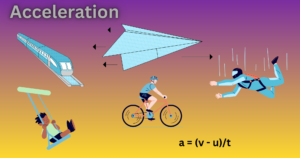
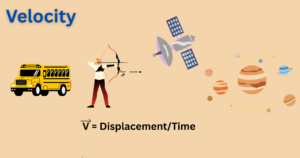
Elasticity: Concept, Cause and Effect of Deforming Force with the Applications Explained
What is Elasticity? Elasticity is the strength providing property for a material. Here ‘’strength’’ means the behavior of opposing the deforming force acting on it. Elasticity is that quality which gives reformation of the original state of a material after … Read more