Interesting Science Videos
Differences between Acid and Base
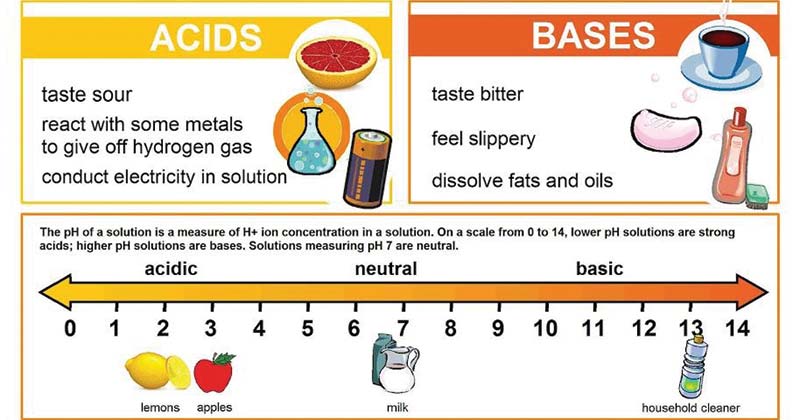
Image Source: Pinterest
Basis |
Acid |
Base |
| Arrhenius concept | An acid is a substance that produces hydrogen ion (H+) as the only positive ion when mixed with water. | A base is a substance that produces hydroxyl ion (OH–) as the only negative ion when mixed with water. |
| Bronsted-Lowry Concept | An acid is a species that can release/donate a proton to another species. | A base is a species that can accept a proton. |
| Lewis Concept | An acid is a species that can accept an electron pair. | A base is a species that can donate an electron pair. |
| Strength | The strength of an acid is based on the concentration of hydrogen ions. | The strength of a base is based on the concentration of hydroxyl ions. |
| Physical nature | Acids are corrosive in nature. | Bases are slippery in nature. |
| Physical state | Acids exist as solid, liquid, and gas-based on temperature. | Bases usually exist in the solid-state except for ammonia which exists as a gas. |
| Taste | Acids are sour in taste. | Bases taste bitter. |
| Dissociation
|
Acids release hydrogen ions (H+) when dissolved in water. | Bases release hydroxyl ions (OH–) when dissolved in water. |
| Dissociation constant | The dissociation constant of a strong acid is -2. | The dissociation constant of a strong base is 12. |
| pH value | The pH value of acid is lower than that of water (7) with an acid of pH 1 being the strongest acid. | The pH value of the base is higher than that of water and with base pH 14 being the strongest base. |
| Test with litmus | Acids turn a blue litmus paper into red. | Bases turn a red litmus paper into blue. |
| Test with phenolphthalein | Phenolphthalein turns colorless in acidic solutions. | Phenolphthalein turns pink in basic solutions. |
| Test with methyl orange | Methyl orange turns red in color in acidic solutions. | Methyl orange turns orange in color in basic solutions. |
| Test with universal indicator | In the universal indicator, yellow and red color indicates acidic solutions. | In the universal indicator, blue and violet color indicates basic solutions. |
| Reaction with metal | Acids react with metals to give H2 gas. | Bases don’t react with metals. |
| Examples | Hydrochloric acid (HCl), Sulphuric acid (H2SO4), Nitric acid (HNO3), Phosphoric acid (H3PO4), Oxalic acid (C2H2O4), Boric acid (H3BO3), Acetic acid (CH3COOH), carbonic acid, (H2CO3), Aluminium chloride (AlCl3), etc. | Sodium hydroxide (NaOH), Potassium hydroxide (KOH), Calcium oxide (CaO), Magnesium hydroxide (Mg(OH)2), Ammonium hydroxide (NH4OH), Pyridine (C5H5N), Histidine (C6H9N3O2), Ammonia (NH3), etc. |
References
- Gautum SD, Pant M, and Adhikari NR (2016). Comprehensive Chemistry, Part 2. Sixth Edition. Heritage Publishers and Distributors Pvt. Ltd.
Internet Sources
- 5% – https://opentextbc.ca/chemistry/chapter/15-2-lewis-acids-and-bases/
- 3% – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Phenol_phthalein
- 3% – https://brainly.com/question/2624790
- 2% – https://www.microchemicals.com/products/etchants.html
- 2% – https://quizlet.com/136496265/chapter-18-flash-cards/
- 1% – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Acid%E2%80%93base_reaction
- 1% – https://chem.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/General_Chemistry/Map%3A_A_Molecular_Approach_(Tro)/16%3A_Acids_and_Bases/16.04%3A_Acid_Strength_and_the_Acid_Dissociation_Constant_(Ka)
- 1% – https://brainly.com/question/3458136
- 1% – https://answers.yahoo.com/question/index?qid=20070919080405AAvP2Rr

Very nice. Keep it up.
It’s hard to say
Good