The pharmaceutical sector has recently made significant progress, focusing on enhancing drug delivery methods to improve the bioavailability of diverse drugs. Nanoemulsions, utilized for medication delivery, offer several advantages. Their small droplet size, typically ranging from 20 to 200 nanometers, creates a substantial interfacial area, promoting the dissolution of drugs and thereby enhancing the solubility and bioavailability of poorly water-soluble substances.

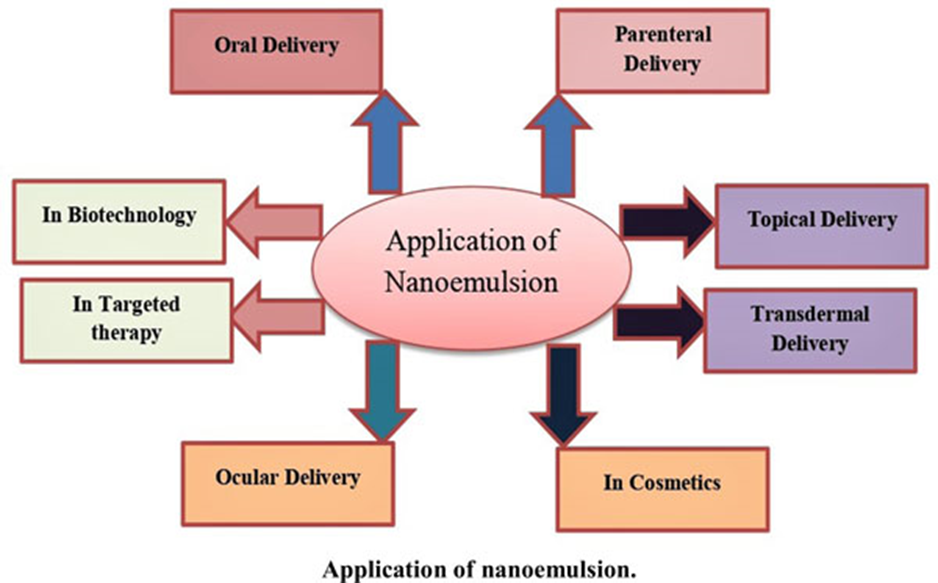
Nanoemulsions serve as a versatile platform for drug administration across different therapeutic areas, as they can encapsulate both hydrophilic and hydrophobic medications. These nanoemulsions can be formulated in various dosage forms, such as gels, creams, foams, aerosols, and sprays, employing cost-effective standard operational processes. They can be administered through different routes, including oral, topical, intravenous, intrapulmonary, intranasal, and intraocular.
This technology explores nanoemulsion formulation and production methods, underscoring the crucial role of surfactants and cosurfactants in crafting stable formulations. The careful selection of components and production techniques is pivotal in tailoring nanoemulsions to specific medication delivery needs, ensuring the stability and effectiveness of the final product.
Nanoemulsions represent cutting-edge technology with substantial potential to enhance medication bioavailability across diverse therapeutic contexts. Their capacity to improve drug solubility, stability, and delivery positions them as valuable tools in developing innovative pharmaceutical formulations. As advancements continue in this field, nanoemulsions are poised to play a critical role in elevating medication delivery standards and improving patient outcomes.
Interesting Science Videos
Advantages of Nanoemulsions in Drug Discovery
Enhanced Bioavailability of Poorly Soluble Drugs: Nanoemulsions play a crucial role in overcoming the challenge of poor solubility often encountered with drug compounds. Their small droplet size provides a larger interfacial area, facilitating improved dissolution of poorly water-soluble drugs. This enhanced solubility leads to increased bioavailability, ensuring that a greater proportion of the administered drug reaches its target site, thus potentially improving therapeutic efficacy.
Versatility in Drug Administration: Nanoemulsions offer versatility in drug delivery methods, making them suitable for various therapeutic applications. They can encapsulate both hydrophilic and hydrophobic drugs, allowing for a wide range of formulations tailored to specific drug properties and administration routes. Whether administered orally, topically, intravenously, or through other routes, nanoemulsions provide a flexible platform for delivering drugs effectively to their intended targets.
Reduced Surfactant Requirement: Compared to conventional emulsion systems, nanoemulsions require lower amounts of surfactants to stabilize the droplets. This reduction in surfactant usage not only improves cost-effectiveness but also minimizes potential side effects associated with surfactant exposure, making nanoemulsions a safer option for drug delivery.
Improved Transdermal Absorption: Nanoemulsions have demonstrated significant advantages in transdermal drug delivery. Studies have shown that drugs formulated in nanoemulsions, such as celecoxib, exhibit higher absorption rates when applied to the skin compared to traditional oral formulations. This enhanced transdermal absorption offers opportunities for developing novel therapies and improving patient compliance.
Extended Drug Retention Time: Nanoemulsions prolong the retention time of drugs at the target site, which can be beneficial for sustained therapeutic effects and reduced dosing frequency. By minimizing systemic exposure and enhancing local drug concentrations, nanoemulsions help minimize side effects and improve patient tolerance to medications.
Optimized Therapeutic Activities: Research on nanoemulsion-based formulations of drugs like aspirin and flurbiprofen has demonstrated enhanced therapeutic activities, including improved anti-inflammatory and analgesic effects. This optimization of therapeutic activities suggests the potential of nanoemulsions to improve treatment outcomes and patient care in various disease conditions.
Reduced Drug Amounts Required: Nanoemulsions enable the use of lower drug doses while maintaining therapeutic efficacy. This is attributed to their ability to enhance drug penetration, increase bioavailability, and prolong drug retention time at the target site. By reducing the amount of drug needed for treatment, nanoemulsions offer potential cost savings and minimize the risk of adverse effects associated with high drug doses.
Broad Spectrum Antimicrobial Activity: Nanoemulsions exhibit broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity, making them promising candidates for antimicrobial drug discovery. Their ability to destabilize microbial cell membranes and effectively target a wide range of microorganisms suggests potential applications in combating infectious diseases and addressing antimicrobial resistance challenges.
Efficient Eradication of Microorganisms: Positively charged nanoemulsions, such as those containing amoxicillin, have demonstrated efficient eradication of microorganisms like Helicobacter pylori. By leveraging electrostatic interactions and thermodynamic fusion with microbial membranes, these nanoemulsions offer targeted and effective antimicrobial action, paving the way for the development of novel antimicrobial therapies.
Application of Nanoemulsion in Drug Discovery
Anti-Microbial Nanoemulsions
Nanoemulsions with oil-in-water droplets exhibit potent antimicrobial properties, targeting a wide range of pathogens including bacteria, enveloped viruses, fungi, and spores. The mechanism involves the fusion of nanoemulsion droplets with lipid-containing organisms, releasing energy that disrupts microbial cell membranes, leading to cell lysis. This broad-spectrum activity positions antimicrobial nanoemulsions as promising agents in the fight against various infectious agents.
Nanoemulsions in Cancer Therapy
In the domain of cancer therapy, nanoemulsions serve as versatile vehicles, particularly in chemotherapy. Administered through intramuscular and intratumoral injections, nanoemulsions prolong the release of anti-cancer drugs. Furthermore, they enhance drug transport through the lymphatic system, contributing to improved therapeutic outcomes. The adaptability of nanoemulsions positions them as valuable assets in addressing the complexities of cancer treatment.
Mucosal Vaccines Using Nanoemulsion
Nanoemulsions play a pivotal role in revolutionizing vaccine administration by enabling needle-free immunization. They effectively deliver recombinant proteins and inactivated organisms to mucosal surfaces. The small droplet size of nanoemulsions enhances the adjuvanting of protein surfaces, facilitating uptake by antigen-presenting cells. This innovation holds great promise in the development of effective and efficient mucosal vaccines.
Nanoemulsions in Cell Culture Technology
Within cell culture technology, nanoemulsions find application in optimizing conditions for cell growth. By increasing the uptake of oil-soluble components, nanoemulsions contribute to improved growth and health of cultured cells. This utilization showcases the adaptability of nanoemulsions beyond therapeutic applications, highlighting their significance in advancing cell culture technology.
Prophylactic Defense Against Bio-Terrorism Attacks
Nanoemulsions play a pivotal role as prophylactic measures against potential bio-terror threats like anthrax and Ebola. The unique properties of nanoemulsions, crafted through methods such as phase inversion or self-emulsification, enable their application in treating contaminated wounds. The versatility of nanoemulsions in targeting a broad spectrum of pathogens makes them a valuable tool in mitigating the impact of bio-terrorism attacks.
Nanoemulsion Applications in Drug Delivery
Nanoemulsion and Drug Targeting: Ongoing research explores the development of nanoemulsion formulations for controlled and targeted drug delivery. Their submicron size facilitates precise targeting, making them particularly promising for applications in cancer treatment. Magnetic nanoemulsions, for instance, demonstrate efficacy in tumor targeting and can induce hyperthermia, showcasing potential applications in photodynamic therapy for cancer treatment.
Drug Delivery via Transdermal Nanoemulsions: Transdermal drug delivery using nanoemulsions has garnered significant interest due to its practicality in systemic circulation for various clinical diseases. Nanoemulsions, with their pleasant feel on the skin, offer an advantageous alternative to oral delivery, minimizing gastrointestinal adverse effects. Efforts are focused on overcoming the skin barrier for improved drug targeting and pharmacokinetics, with nanoemulsions showing promise in enhancing the permeability of drugs like caffeine for transdermal applications.
Drug Delivery via Pulmonary Nanoemulsions: While research in this field is limited, nanoemulsion methods are being explored for pulmonary drug administration. Stable emulsion systems are being developed as alternatives to liposomes for gene transfer, showing promise in gene delivery to pulmonary epithelial cells. Future research in nebulization of submicron emulsions is expected to contribute to advancements in pulmonary drug administration.
Delivery of Parenteral Drugs Using Nanoemulsions: Nanoemulsions serve as efficient carriers for parenteral drug administration, particularly for drugs with low bioavailability. Their ability to dissolve hydrophobic compounds, coupled with sustained and controlled drug release, allows for reduced injection frequency and dosage. Studies demonstrate the potential of nanoemulsion-loaded drugs in treating conditions like colon adenocarcinoma, showcasing improved anticancer activity compared to plain drug solutions.
Delivery of Ophthalmic Drugs Using Nanoemulsions: Nanoemulsions prove valuable in addressing challenges associated with ophthalmic ailments. These formulations enhance ocular bioavailability, allowing for lower dosages and minimizing systemic side effects. Nanoemulsion-based ophthalmic formulations are characterized by their adaptability, providing a more tolerable and less viscous alternative to conventional therapies.
Delivery of Intranasal Drugs Using Nanoemulsions: Intranasal drug delivery, recognized for its noninvasiveness and effectiveness, benefits from nanoemulsion technology. Nanoemulsions facilitate drug penetration through the nasal mucosa, offering a promising route for treating central nervous system disorders. Applications range from treating diseases like Alzheimer’s to developing intranasal vaccines, highlighting the potential of nanoemulsions in advancing drug delivery strategies.
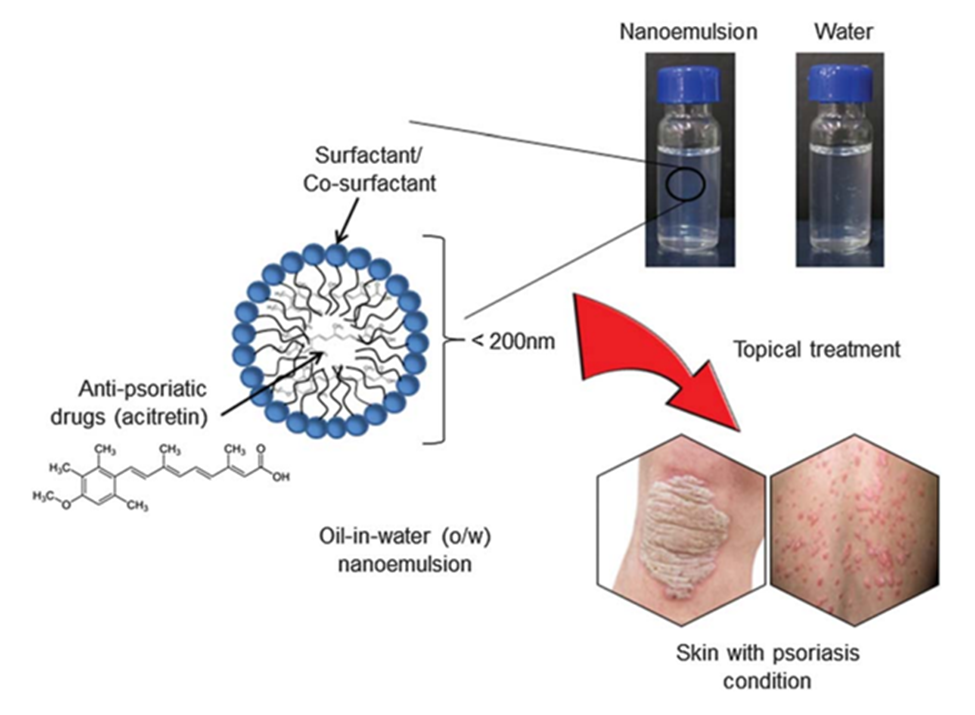
[Image source: https://asasi.upm.edu.my/article/]
Challenges of Nanoemulsions in Drug Delivery
- Stability Issues: Nanoemulsions are prone to stability challenges, particularly due to Ostwald ripening, where larger droplets grow at the expense of smaller ones over time. This phenomenon poses a risk of affecting the long-term stability of nanoemulsion formulations.
- Formulation Variability: Identifying and understanding sources of variability during the development of nanoemulsions is crucial. Variations in composition and manufacturing processes can impact the safety and therapeutic efficacy of the drug product.
- Drug-Loading Capacity: Nanoemulsions may have lower drug-loading capacity compared to other nano-sized formulations, limiting their ability to carry high concentrations of poorly water-soluble drugs. This can pose a challenge in achieving optimal drug dosage.
- Ostwald Ripening Susceptibility: The Ostwald ripening phenomenon remains a significant challenge, particularly for oil-in-water nanoemulsions. Despite efforts to address this issue, long-term stability concerns persist, potentially impacting the shelf life of nanoemulsion-based drug products.
- Influence of Carrier Oils: The selection of appropriate carrier oils plays a crucial role in the effectiveness of nanoemulsions. Variability in the behavior of different oils, including differences in density, viscosity, and polarity, can impact drug solubilization and overall bioavailability.
- Strict Hydrophilic-Lipophilic Balance Adjustment: Traditional manufacturing methods, such as phase inversion temperature (PIT) and phase inversion composition (PIC), require strict hydrophilic-lipophilic balance (HLB) adjustments. This constraint can limit the formulation flexibility and add complexity to the development process.
- Limited Drug Solubility in Some Oils: The solubility of certain drugs in specific oils may present challenges. Some drugs may not be easily solubilized in the chosen carrier oil, requiring careful selection and screening to achieve optimal drug delivery efficacy.
- Need for Rigorous Formulation Optimization: Achieving the desired stability and efficacy of nanoemulsions demands rigorous optimization of the formulation, considering factors such as surfactant concentration, oil type, and manufacturing processes. This optimization process can be resource-intensive.
- Scale-Up Challenges: Transitioning from laboratory-scale production to large-scale manufacturing can pose challenges. The scalability of nanoemulsion production processes and the associated costs and equipment requirements need careful consideration.
References
- Yukuyama MN, Kato ET, Lobenberg R, Bou-Chacra NA. Challenges and Future Prospects of Nanoemulsion as a Drug Delivery System. Curr Pharm Des. 2017;23(3):495-508. doi: 10.2174/1381612822666161027111957. PMID: 27799037.
- https://www.futuremedicine.com/doi/10.2217/nnm-2018-0088
- Sutradhar, Kumar Bishwajit and Amin, Md. Lutful. “Nanoemulsions: increasing possibilities in drug delivery” European Journal of Nanomedicine, vol. 5, no. 2, 2013, pp. 97-110. https://doi.org/10.1515/ejnm-2013-0001
- Preeti, Sambhakar S, Malik R, Bhatia S, Al Harrasi A, Rani C, Saharan R, Kumar S, Geeta, Sehrawat R. Nanoemulsion: An Emerging Novel Technology for Improving the Bioavailability of Drugs. Scientifica (Cairo). 2023 Oct 28;2023:6640103. doi: 10.1155/2023/6640103. PMID: 37928749; PMCID: PMC10625491.
- Russell J. Wilson, Yang Li, Guangze Yang, Chun-Xia Zhao, Nanoemulsions for drug delivery, Particuology, Volume 64, 2022, Pages 85-97, ISSN 1674-2001, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.partic.2021.05.009.
- Preeti, Sharda Sambhakar, Rohit Malik, Saurabh Bhatia, Ahmed Al Harrasi, Chanchal Rani, Renu Saharan, Suresh Kumar, Geeta, Renu Sehrawat, “Nanoemulsion: An Emerging Novel Technology for Improving the Bioavailability of Drugs”, Scientifica, vol. 2023, Article ID 6640103, 25 pages, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/6640103
- Asif Eqbal, Vaseem Ahamad Ansari, Abdul Hafeez, Farogh Ahsan, Mohd Imran, Saquib Tanweer. Recent Applications of Nanoemulsion Based Drug Delivery System: A Review. Research Journal of Pharmacy and Technology. 2021; 14(5):2852-8. doi: 10.52711/0974-360X.2021.00502
