Reducing vs Non-Reducing Sugar- Definition, 9 Key Differences, Examples
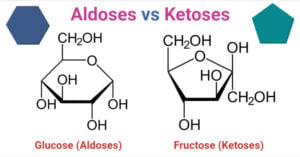
Reducing Sugar Definition Reducing sugar is a type of sugar that consists of a free aldehyde group or a free ketone group, allowing the molecule to act as a reducing agent. All monosaccharides are reducing sugars, and so are some … Read more