Chemistry Lab Glassware is an essential for any educational, chemical, analytical, research, or pharmaceutical laboratory. It is also known as Scientific Glassware and is usually used for carrying out various scientific experiments, storing chemicals or specimens, and taking measurements. The lab equipment that are often used in studies are classified according to their function. Some tools are used for carrying materials, others for combining chemicals, and yet others for heating.

Let us talk about the chemistry lab glassware frequently used.
Interesting Science Videos
Beakers
A beaker is a basic container for stirring, mixing, and heating liquids that is often used in labs. Beakers are usually cylindrical in form, with a flat bottom and a pouring lip.
Uses of Beakers
- Beakers can be used to hold liquid or solid samples, as well as as a reaction container.
- They are also used to collect filtrates and liquids from titrations.
- It is used to mix the liquid.
- It’s handy as a reaction container.
- Beakers are used to capture liquids in experiments that produce a liquid product.
Boiling Flasks
Boiling flasks are used to heat and boil liquids. The flasks are built with spherical bodies and long, thin necks to allow even heat distribution and decrease evaporation. Boiling flasks are often composed of borosilicate glass, which is resistant to heat stress and chemicals. Some boiling flasks have rounded or conical bottoms and require assistance to stand erect, whilst others have flat bottoms and may stand alone.

It is safe to heat boiling flasks to a high temperature that will bring the liquid inside to a boil. As a result, boiling flasks are made of borosilicate glass, which can withstand temperatures of about 500°C. Boiling flasks are frequently placed within heating mantles in order to achieve these temperatures.
Uses of Boiling Flasks
- The flask is designed to ensure that the solution inside it is uniformly heated. The broad bottom and thin neck allow the solution to be readily swirled inside without spilling.
- They have typically been used in studies to hold onto chemical solutions and heat them as needed.
Burettes
Burette, a laboratory device used in quantitative chemical analysis to quantify the volume of a liquid or a gas. It is made out of a graded glass tube with a stopcock (turning plug, or spigot) at one end. The stopcock is at the bottom of a liquid burette, and the precise volume of liquid dispensed may be established by reading the graduations written on the glass tube at the liquid level before and after dispensing. The stopcock in a gas burette is located at the top; the burette’s tube is filled with a fluid, such as water, oil, or mercury, and the bottom of the tube is connected to a reservoir of the fluid.

Uses of Burette
- Burettes are commonly employed in the laboratory for quantitative analysis and titration.
- They are also employed in a variety of different industrial applications, including pharmaceuticals industry for drug concentration verification.
- Used for measuring the acidity levels of food liquids in the food industry
- To test the concentration of components in a safe proportion in cosmetics
- Impurities in biofuel are measured throughout the manufacturing process.
- Analyzing bodily fluids such as blood and urine for medical diagnosis.
Condensers
Condensers are frequently employed in reflux, when hot solvent vapors from a heated liquid are cooled and allowed to drip back. This decreases solvent loss, allowing the mixture to be heated for longer periods of time.
In distillation, condensers are used to cool heated vapors, condensing them into liquid for separate collection. An air or Vigreux condenser is typically employed in fractional distillation to reduce the pace at which the hot vapors rise, allowing for greater separation of the various components in the distillate.

Uses of Condenser
- Condensers have a variety of applications in the chemical laboratory, although they are most typically employed in processes such as distillation, reflux, and extraction.
- Condensers are used in distillation to cool heated vapors and condense them into liquid for separate collection.
- Condensers are employed in the reflux process, which involves cooling hot solvent vapours from a heated liquid before dripping them back into the reaction. Simply allowing the mixture to heat up for a longer amount of time lowers solvent loss.
Conical Flasks
A conical flask is a kind of laboratory flask with a wide, flat bottom and an inverted cylindrical neck that is used for transportation, storage, and mixing in scientific experiments. It is sometimes referred to as an Erlenmeyer flask, a titration flask, or an E-flask.
These flasks are generally composed of heat-resistant borosilicate glass, which aids in thermal stress resistance. They can be used in chemical, biology, or microbiology laboratories to do scientific research.

Uses of Conical Flasks
- Conical flasks are used in chemistry, biology, and microbiology to heat, mix, and transfer chemicals or reagents.
- In chemistry, Erlenmeyer flasks are used for a variety of purposes in the laboratory. Because of its uneven form, it is ideal for spinning fluids. As a result, it is utilized in titration experiments.
- Conical flasks are also used to boil liquids. The top of the Erlenmeyer flask aids in condensing the solvent. The small neck and reduced solvent loss can further improve the capability of recrystallization.
- Conical flasks are used in biology to create microbial culture that is required for tissue culture or DNA extraction.
- Conical flasks are also used in the microbiology laboratory to boil and sterilize culture medium when making culture plates.
Desiccators
A desiccator is an airtight container that is used to dry samples and store hygroscopic materials at atmospheric or vacuum pressure. It is also known as dehumidifiers or dehydrators. It’s also used to keep hot samples and things like crucibles cold. It employs an appropriate drying agent (desiccant).
Desiccators are essential for chilling and storing hygroscopic materials, which accumulate moisture when left outside in the working environment.
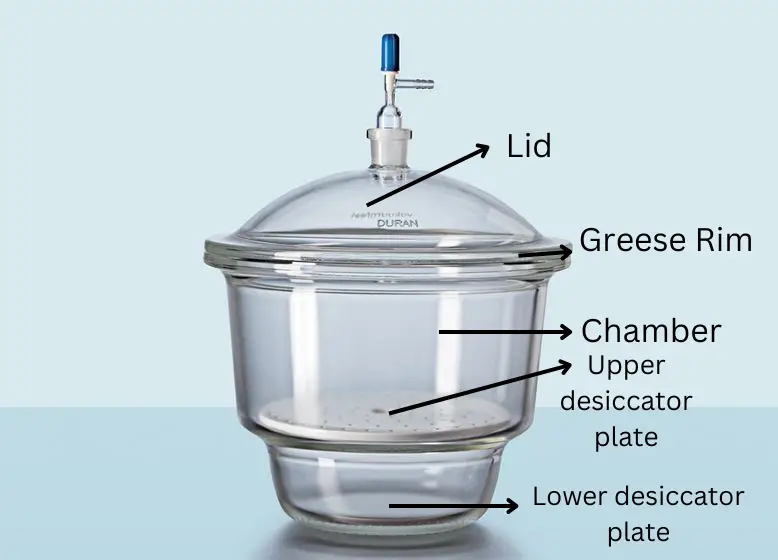
Uses of Desiccators
- To eliminate moisture from substances, utilized in the preparation of standard solutions such as NaCl, KCl, and oxalic acid.
- For storing commodities that require continual weighing under dry circumstances, such as soil, dissolved solids, and so on.
- For the long-term storage and cooling of hygroscopic substances such as sodium chloride and sodium hydroxide crystals.
- To determine the dry weight of molecules such as proteins, carbohydrates, and so on.
- For drying heat-labile compounds such as proteins and microorganisms (often starting culture).
Distillation Flask
Distilling flasks are used to separate mixtures of two liquids having differing boiling points. A wide range of types and capacities are available to support distillation processes of different complexity. A long neck distillation column, a side arm for condensation, and a circular bottom for uniform heat distribution are typical elements of flask design. Distilling flasks, also known as distillation flasks, are laboratory flasks that are part of larger distillation assemblies used for the separation and/or purification of liquids or liquid mixtures with differing boiling points.

Uses of Distillation Flasks
- Distillation flasks are used to confine and heat the liquid(s) that need to be purified.
- Separation and purification of miscible liquid mixtures in organic chemistry.
- Removal of solvents and/or drying of solid residues
- Distilling liquids from polymers and petroleum products
- Removal of particles or other solid pollutants
- As part of a water purification system for producing distilled water for laboratory usage.
Erlenmeyer Flask
Erlenmeyer flasks are conical flasks with large flat bottoms and tapering necks. The flasks are designed for a wide range of liquid handling activities in the laboratory, including pouring, mixing, storing, and suspension cell culture.
Erlenmeyer flasks are available in a variety of sizes and with wide or narrow mouth designs. There are sterile and non-sterile Erlenmeyer flasks available. The flasks are normally constructed of glass or plastic and are manufactured from a variety of materials. Titration flasks are called Erlenmeyer flasks after the inventor, Emil Erlenmeyer.
Flat Bottom Flask
Flat bottom flasks are spherical flasks with a single neck that are used for heating in distillation or other chemical operations. They are not as strong as round bottom flasks, but they do not have the sharp and dangerous corners of an Erlenmeyer Flask. Their flat bottoms let them to stand on a hot plate, shelf, or table. These can be used to create solutions as well as to confine or gather them. They may also be used to measure the volume of chemicals, samples, solutions, and so forth. They are also utilized in chemical reactions and other operations such as mixing, heating, cooling, dissolving, precipitating, boiling, distilling, and analyzing.

Uses of Flat Bottom Flask
- They can be used to mix liquids and conduct various chemical experiments in the same way as round-bottomed flask can. This might include monitoring how various compounds react to one another when heated with a flame.
- The flask can be left standing upright on a stand that is covering the flame if you have previously combined certain ingredients and want to watch how they respond over the top of a Bunsen Burner. The heat may be diffused evenly throughout the liquid due to the flask’s flat bottom.
- It may be used to keep liquids in a refrigerator or elsewhere because there is no chance of them toppling over and leaking.
Florence Flask
A Florence flask (also known as a boiling flask) is a kind of flask used as a chemistry lab glassware. It can be used to hold chemical solutions. A Florence flask features a spherical body with a single long neck and a round or flat bottom. A Florence flask with a flat bottom may stand erect on its own on a flat surface; flasks with circular bottoms require help to stand upright. It is made in a variety of glass thicknesses to withstand various sorts of use and to provide even heating. They are frequently manufactured of borosilicate glass coated with alkali to avoid cracking or defacing of the glass.

Uses of Florence Flask
- The flask is designed to facilitate homogeneous heating of the solution contained within it. Because of the broad bottom and small neck, it allows the solution to be readily swirled inside without spilling.
- They are commonly used in studies to hold onto chemical solutions and heat them as needed. A Florence flask is typically one liter in capacity, making them substantial pieces of glassware.
Funnel
A funnel is a pipe with a thin stem and a large, generally conical mouth. It is used to direct liquids or fine-grained material into small-mouthed containers. Without a funnel, there would be a lot of spillage.
Stainless steel, glass, or plastic are the most common materials used to make funnels. The material utilized in its construction should be strong enough to sustain the weight of the substance being conveyed while also not reacting with it.

Uses of Funnel
- Funnels are commonly used in laboratories to filter, fill, decant, or move liquids or powders from one vessel to another.
- Funnel is required to transfer the chemicals without spillage or wastage.
Glass Rods
Glass rods are thin, cylindrical rods made of glass that are commonly used in laboratories. They can be used to transport a tiny amount of liquid between containers or apply chemicals to surfaces in addition to stirring liquids or suspensions.
Glass rods exist in a range of shapes and sizes, each with its own set of features and applications. The borosilicate glass standard glass stirring rod is a typical variety that is used for general liquid stirring and mixing. The micro glass rod is a new type that is more delicate and thin than regular glass rods and is used for precision activities such as transferring tiny quantities of liquid or manipulating microscopic particles. High-purity quartz glass rods are also used in high-temperature applications due to their exceptional heat resistance. Glass rods are commonly used in physics and chemical tests due to their neutrality, hardness, and versatility.

Uses of Glass Rod
- Glass rods are employed in a variety of scientific settings due to their versatility, hardness, and inertness.
- Glass rods are commonly used to stir or combine liquids. Glass rods are the ideal choice for this operation since they can be sanitized rapidly to eliminate contamination and are chemically resistant.
- Glass rods can also be used to transfer small amounts of liquid between containers, such as when doing dilutions or reactions. Because of their small diameter, glass rods are ideal for this.
- Furthermore, glass rods can be used to apply materials to surfaces, such as when coating slides with a microscope sample. The flat surface of glass rods ensures that the material is applied equally and consistently.
- Specialized glass rods with flattened or hooked ends are another alternative for scraping or recovering materials. Because of their durability and versatility, glass rods are a vital equipment in a laboratory environment for a number of applications such as glass stick, glass stirrer, and so on.
Glass Tubes
Many labs and industrial settings utilize laboratory glass tubing to link other pieces of glassware or equipment as well as to carry or distribute chemicals, solvents, liquids, gases, and other goods. For the most demanding uses, it is often made of borosilicate glass. Borosilicate has strong heat, thermal shock, and chemical resistance, as well as low-leaching extractables, good mechanical strength, and a low coefficient of expansion. Because soda lime glass tubing and flint glass tubing have lower softening points, they are often employed for less demanding applications. Laboratory glass tubing is available in a range of diameters, lengths, and wall thicknesses depending on the intended application.
Uses of Glass Tubes
- Glass tubes are used in organic synthesis, fractionation, distillation, or titration
- Theses are also employed to set up chromatographic or filter columns.
- It is also utilized in gas delivery and collection experiments.
Graduated Cylinders
A graduated cylinder is a type of scientific glassware used to measure liquid volume. It is made out of a cylindrical tube with a small, vertical scale marked on the outside that allows the user to accurately read the volume of the liquid. The size of the graduations and the class of the cylinder determine the accuracy of a graded cylinder. Graduated cylinders are available in a variety of diameters, ranging from 10 milliliters (mL) to 2,000 mL. The maximum amount of liquid that the cylinder can hold is determined by its size. When utilizing a graduated cylinder, it is critical to read the scale at the bottom of the meniscus.

Uses of Graduated Cylinder
- Measuring cylinders are used to determine the volume of liquids, solids, and mixes.
- They may also be used to mix liquids and pour liquids from one container to another.
- Graduated cylinders are composed of glass or plastic and available in a range of sizes.
Ignition Tubes
One kind of equipment used in laboratories is the ignition tube. It is a laboratory tube that is used similarly to a boiling tube but is not as big or thick-walled. It is typically used to store small amounts of things that are being directly heated by a Bunsen burner or other heat source. Because of their narrow bore, ignition tubes can be difficult to clean. When used to rapidly heat items, some char may adhere to the walls as well. They are often discarded. It is composed of high-quality Borosilicate Glass.

Uses of Ignition Tube
- It is used to test for decomposition by severely heating solid materials.
- This sort of tube is mostly used in the sodium fusion test.
Pipettes
A pipette is a laboratory instrument used to measure or dispense small amounts of liquid in milliliters (mL) or microliters (μL). Glass pipettes are made of borosilicate glass, plastic pipettes are made of polyethylene terephthalate (PET), and electronic pipettes are operated by microprocessors. Plastic and glass pipettes are often used to measure quantities less than 1 milliliter (mL). The pipette’s operation is primarily dependent on two mechanisms: the air displacement technique and the positive displacement method.
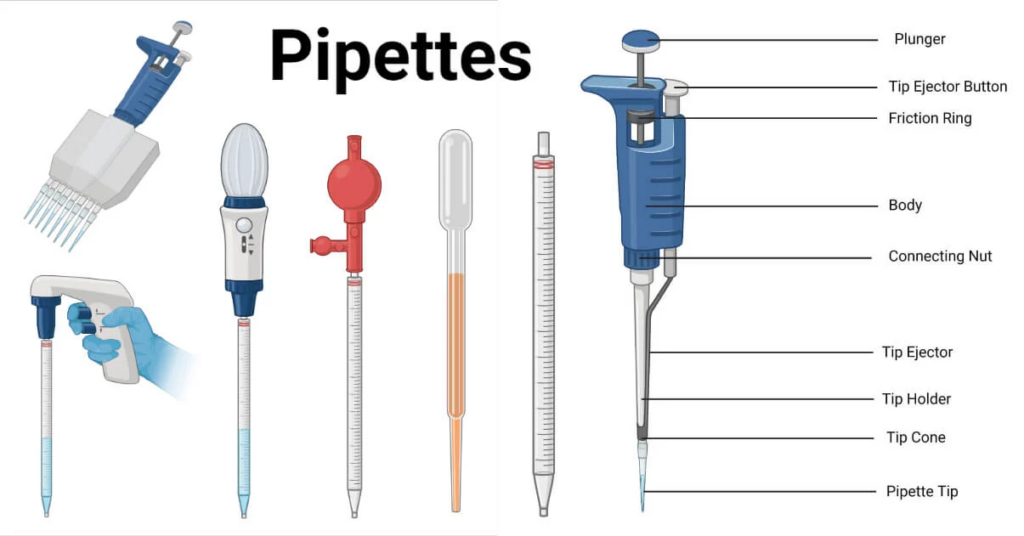
Pipettes of various sizes and shapes are frequently required in laboratories to handle a variety of sample quantities and applications.
Micropipettes: Micropipettes are precision tools used to handle tiny liquid quantities, often in the microliter range. They are essential in molecular biology, microbiology, and other life sciences.
Multichannel Pipettes: Pipettes with numerous channels enable for the simultaneous pipetting of many samples, increasing efficiency in high-throughput research. They are commonly utilized in diagnostic and research facilities.
Serological Pipettes: Serological pipettes are employed in cell culture and routine laboratory operations for precise measuring and dispensing of greater amounts of liquids.
Uses of Pipettes
- It aids in the equal dispersion of cells during cell seeding and prevents foaming and bubble formation.
- It facilitates the exchange of media between T-flask cell cultures while maintaining sterility and preventing contamination.
- 96 well microplates, which are commonly used in microplate applications such as ELISA, PCR, or cell culture, are compatible with multichannel pipettes of 8 or 12-channel varieties.
- Electronic pipettes are used to aliquot a reagent into numerous dosages, a technique known as multi-dispensing.
- Serological pipettes are used in traditional laboratory settings as well as applications involving cell and tissue culture.
Reagent Bottles
A reagent bottle is a specific container used in labs to store chemical reagents or solutions for research and testing. Its robust construction ensures the safe storage, transportation, and use of volatile, corrosive, or otherwise dangerous compounds. Laboratory Reagent Bottles are classified according to their material, size, and opacity. These features enable more customization and adaption to unique laboratory requirements. There are primarily two sorts of bottles based on their materials: plastic and glass bottles.

Uses of Reagent Bottles
Due to their indispensable nature and adaptability, these laboratory bottles are essential to a wide range of industries, including scientific laboratories and the medical and healthcare sectors.
These bottles are widely used in the medical and healthcare sectors.
- They provide safe storage for clinical chemistry reagents used in a variety of diagnostic procedures including as calcium, urea, total protein, and lithium.
- It may be used for storage as well as to protect light-sensitive materials.
- These bottles help to a well-organized and efficient laboratory environment by serving as storage containers for liquid or powder-form chemicals. Their specialized caps or stoppers are meant to keep stored compounds stable and pure, expediting lab activities and promoting a safe and organized environment.
Retort
A retort is a glassware apparatus used in chemical laboratories for distillation or dry distillation of substances. It is made up of a spherical vessel with a long downward-facing neck. The distilled liquid is poured in the vessel and heated. The neck functions as a condenser, enabling evaporated vapors to condense and travel along the neck to a collection vessel underneath.
Retort furnaces may be used for a variety of industrial purposes in addition to heat treatment.
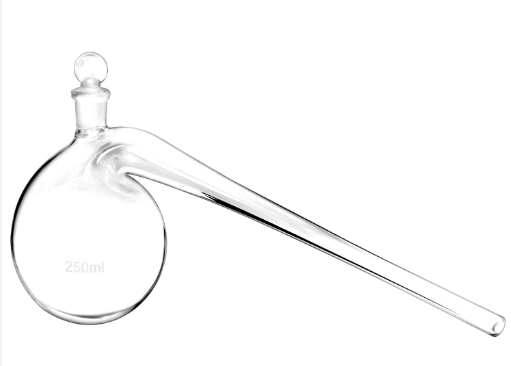
Use of Retort
- A retort is a device used in chemical laboratories for distillation or dry distillation of substances.
Round Bottom Flasks
Round bottom flasks with short or long necks are commonly used in chemical and biological research. Round bottom flasks are designed for consistent heat distribution and are used for distillation, chemical reactions, heating liquid samples, and storage needs. The spherical containers, made of strong glass, will distribute encountered tension uniformly across surfaces to prevent breaking. The glassware is a vital item in reflux setups since it is temperature resistant. Round-bottom flasks with ball-and-socket joints are used as receiving flasks in rotary evaporators because the joints allow for simple handling of flasks without the risk of freezing and do not require lubrication or sleeve joints.

Uses of Round Bottom Flask
- The spherical bottoms of these flasks enable for more equal heating and/or boiling of liquid. As a result, round-bottom flasks are often utilized in situations where the contents are heated or boiled. Chemists typically utilize round-bottom flasks in distillation as distilling flasks and receiving flasks for the distillate.
- Round-bottom flasks are frequently employed by chemists to confine chemical processes, particularly for reflux setups and laboratory-scale synthesis.
Test Tubes
In a laboratory, test tubes are portable tubes used for mixing or heating substances. They are generally constructed of glass or plastic and are open at the top and rounded at the bottom. Some are intended to be reused, while others are intended to be discarded. Test tubes are a form of labware that is also known as culture or sample tubes depending on the use. Glass, plastic, metal, and ceramic are all common test tube materials. Glass and plastic are the most common materials; some are meant for reuse, while others are disposable.

Uses of Test Tubes
- Chemists use test tubes to mix, heat, and/or store tiny quantities of chemicals for tests and laboratory research.
- Biologists use them to develop and manipulate different species, fluids, and materials.
- Some test tubes, such as those used for coagulation screening, include prepared chemicals.
- Blood collection tubes in hospitals, labs, and other medical institutions use colored lids or stoppers (screw caps) to distinguish different kinds and screenings.
Volumetric Flasks
A volumetric flask is a type of scientific glassware used for solution preparation. A volumetric flask is a bulb with a flat bottom and an extended neck calibrated to retain a certain volume at a point on the neck. Because its mark specifies a precise volume measurement, the flask is also known as a graded flask or measuring flask. Most volumetric flasks are clear glass or plastic, with the exception of amber-colored flasks used to prepare light-sensitive solutions.

Uses of Volumetric Flasks
- It is used to calculate the volume of a liquid, as well it is also utilized in the manufacture of other mixes.
- When determining the volume of liquid, utilize the marks on the volumetric flask’s neck as a reference. We can determine the volume of the liquid by monitoring a curve that is either ascending or descending.
- Volumetric Flask may also be used to prepare solutions.
Watch Glass
Watch glasses are tiny, flat, circular glassware items. This watch glass constructed of Pyrex glass. A watch glass is a spherical, concave glass dish used in chemistry for evaporation. It may also be used to weigh substances and as a flask or beaker lid. They are mostly used to dry and weigh solid substances, as well as to cover containers like TLC development chambers. Watch glasses come in a variety of sizes.

Uses of Watch Glass
- It is made of strong glass and is ideal for quantitative analysis in laboratories. In biochemical analysis, for example, two watch glasses are used to create a culture chamber for suspension drop culture investigations.
- The watch glass can be used to cover the beaker, evaporating dish, crystallization dish, funnel, and other instruments to keep dust out and the substance clean during operation.
- It is utilized during the sublimation process to keep the detached material at the bottom of the watch glass. It can be used to replace the balance’s weighing pan for weighing corrosive chemicals.
Thistle Tube
A thistle tube, also known as a thistle funnel, is a laboratory glassware item that has a long tube shaft and a reservoir bulb with a flared rim on top. These funnels make it possible to precisely position small amounts of chemicals in an existing system or equipment, making it easier to introduce fresh ingredients to burets and narrow neck containers. Thistle tube funnels limit the likelihood of a reaction developing too rapidly and spilling over.

Uses of Thistle Tube
- Chemists commonly utilize thistle tubes to introduce liquid to an existing system or instrument.
- Thistle funnels are used to transfer little amounts of liquid to a particular position.
Capillary Tube
A capillary tube is a type of chemistry lab device used to calculate the melting point temperature of chemical compounds. It is a thin pipe with inner diameters ranging from 0.5 to 3 mm and lengths ranging from 1 to 6 mm. They are used to keep a sample of the chemical material whose melting point is being determined within the melting point equipment, also known as a thiele tube.

Use of Capillary Tube
- It is used to handle sample for the determination of melting point.
References
- Helmenstine, Anne Marie, Ph.D. “Chemistry Glassware Names and Uses.” ThoughtCo, Apr. 5, 2023, thoughtco.com/chemistry-glassware-names-and-uses-606047.
- https://chemglass.com/chemistry-laboratory-glassware-kits
- https://www.chem.ucla.edu/~gchemlab/lab_glassware_web.htm
- https://conductscience.com/specimen-lab/glassware/
