Concave and convex are the most common descriptors used to describe a shape’s outline or surface. “Concave” and “convex” refer to the curvature of objects or mathematical functions. The terms are not commonly used in normal conversation, but they are crucial in science and mathematics. Convex and concave are commonly used words when discussing mirrors, eyeglass lenses, and contact lenses.
Interesting Science Videos
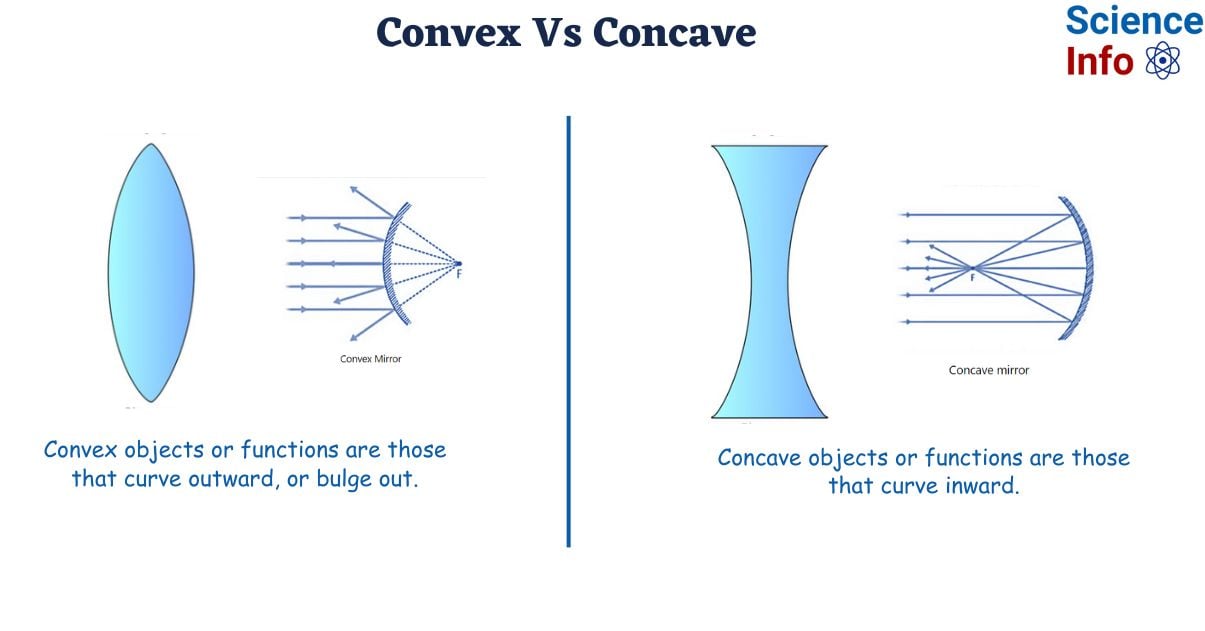
Convex
Convex objects or functions are those that curve outward, or bulge out.
We typically use the term convex to describe processes related to lenses, mirrors, and reflection. A convex mirror will make you appear smaller because of the way light reflects back from it. Convex lenses could be used in microscopes, magnifying glasses, or spectacles. Convex is also used as a noun in mathematics and geometry, referring to a specific form of shape or externally curved line.
Concave
Concave objects or functions are those that curve inward. In simple terms, it is hollow or bent in, similar to a cave.
We most usually use concave to explain phenomena related to lenses, mirrors, and reflection. A concave mirror, for example, will make you appear taller because of how light bounces off of it. Concave lenses may be used in telescopes, binoculars, cameras, or eyeglass lenses. Concave may be used in less technical descriptions of something that curves inwards, such as a crater or pothole, or the stomach of an extremely thin person.
Let us discuss about convex and concave in different aspects.
Convex and Concave Mirrors
Mirrors are surfaces that reflect nearly all incident light rays that strike their surface. The mirror’s surface might be either plane or curved. Mirrors are classified into two types based on this criteria: spherical mirrors and plane mirrors. Plane mirrors have flat, polished reflecting surfaces, whereas spherical mirrors have curved reflecting surfaces. Spherical mirrors are classified into two types based on their curved reflecting surface: concave and convex.
Convex Mirror
When the cut part of the hollow sphere is painted from the inside, the outer surface becomes the reflecting surface. This type of mirror is referred to as convex. A convex mirror is a spherical mirror with an outwardly curved reflecting surface.
It is also known as a diverging mirror because the light that reflects through its surface diverges in numerous directions but appears to meet at certain points, forming a virtual, erect picture of diminished size.
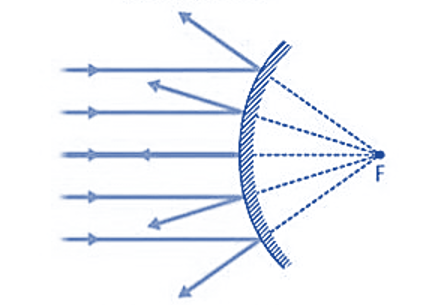
Properties of Convex Mirrors
- A convex or diverging mirror, also known as a diverging mirror, diverges light when it strikes its reflective surface.
- Convex mirrors provide virtual, erect, and diminished images regardless of the distance between an object and the mirror.
Application of Convex Mirrors
- Convex mirrors are used inside buildings to allow people to see around corners and avoid collisions.
- Convex mirrors are employed for security, while diverging mirrors are used in a variety of settings. They are located near ATMs so that bank customers can see if someone is following them.
- Convex mirrors are also utilized in a variety of other applications, including street light reflectors, because they can diffuse light across larger regions.
- Convex mirrors used in vehicles: Convex mirrors are widely utilized as rear-view mirrors in autos and vehicles because they can diverge light beams and create virtual pictures.
- Uses for the convex mirror in a magnifying glass: These mirrors are commonly used to make magnifying spectacles. In industries, a magnifying glass is made by putting two convex mirrors back to back.
Formation of Image in Convex mirror
| Position of the Object | Position of the Image | Image Size | Nature of Image |
| At infinity | At the focus (F), behind the mirror | Highly diminished, point-sized | Virtual and erect |
| Between infinity and the pole (P) | Between P and F, behind the mirror | Diminished | Virtual and erect |
Concave Mirror
If a hollow spherical is sliced into parts and the outer surface of each piece is painted, it becomes a mirror with the inner surface serving as the reflecting surface. This forms a concave mirror. A concave mirror, also known as a converging mirror, is one that is bent toward the inward side in the middle.
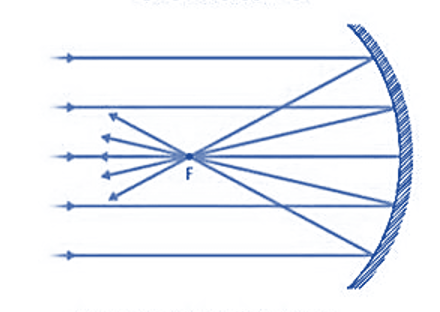
The equation for these mirrors determines the position and correct size of the object. In a concave mirror, the angle of incidence is not equal to the angle of reflection. Furthermore, the angle of reflection in this case is determined by the surface on which the light falls.
Properties of Concave Mirrors
- After reflection, light converges at a point where it strikes and reflects back from the concave mirror’s reflective surface. Hence, it is also known as a converging mirror.
- When the converging mirror is placed very close to the object, an enlarged and virtual image forms.
- However, if we increase the distance between the object and the mirror, the image’s size decreases, and real.
Application of Concave Mirrors
- Torchlights employ concave mirrors to reflect and concentrate light rays. These mirrors focus light beams, increasing their brightness and intensity, making them excellent for illumination.
- These are used as Shaving and Makeup Mirrors since these mirrors are made to enhance lighting and magnify users’ reflections, which facilitates precise work and close inspection of small details.
- Also used as Solar Concentrators. Solar concentrators employ concave mirrors to concentrate solar energy at a single point, which can be used to heat fluids in industrial settings or to generate power.
- Concave mirrors are commonly employed in reflecting telescopes, such as Newtonian telescopes, to gather and focus light from various celestial objects, resulting in high-quality views of stars and distant galaxies.
Formation of Image in Concave Mirror
| Position of the Object | Position of the Image | Image Size | Nature of Image |
| At infinity | At the focus (F) | Highly diminished, point-sized | Real and inverted |
| Beyond the center of curvature (C) | Between F and C | Diminished | Real and inverted |
| At the center of curvature (C) | At C | Same size | Real and inverted |
| Between C and F | Beyond C | Enlarged | Real and inverted |
| At the focus (F) | At infinity | Highly enlarged | Real and inverted |
| Between F and the pole (P) | Behind the mirror | Enlarged | Virtual and erect |
Difference Between Convex and Concave Mirror
A convex mirror forms a diminished image, but a concave mirror, depending on the object’s position, either forms an enlarged or diminished image. This is the primary difference between convex and concave mirror. The following is the main difference between concave and convex mirrors:
| Convex Mirror | Concave Mirror | |
| Shape | Convex mirrors feature a reflecting surface that curves outward. | Concave mirrors have a reflecting curved surface bent inwards, so they face the center of the sphere |
| Mirror Coating | A convex mirror coating is on the inner side of its spherical surface. | The concave mirror coating is applied to the exterior side of the spherical surface. |
| Alternating Name | Also known as diverging mirror. | Also known as converging mirror. |
| Focus | The focus is behind the mirror. | The focus is in front of the mirror. |
| Focal Length | The focal length is positive. | The focal length is negative |
| Image Formation | The image formed is virtual, erect, and diminished. | The image formed is real, inverted, and enlarged (except when the object is between Pole and Focus, where the image is virtual, erect, and enlarged). |
| Image Projection | Images cannot be projected onto a screen since they are virtual. | Images can be projected onto a screen as if they were real. |
| Image size | Always smaller than object. | Larger or smaller depending upon the position of object. |
| Center of Curvature | Behind the mirror. | In front of the mirror. |
| Effect on parallel rays | Diverges away | Converges to a focal point |
| Magnification | Positive | Negative |
| Applications | Convex mirrors are often used as sideview or rearview mirrors in vehicles because they provide a broader field of view. | They are employed in reflecting telescopes, shaving mirrors, torchlights, and other applications because they magnify the image of the object. |
[Image source: https://www.simply.science/]
Convex and Concave Lens
Convex Lens
Convex lenses, also referred to as converging lenses, are transparent optical devices with a curved shape that extends outward from the center and descends inward toward the borders. Because the lens is bigger in the middle than at the sides, it can converge parallel beams of light that pass through it.
Types of Convex Lens
- Biconvex Lens: The lens has a form with bulges toward the center on both sides. It is frequently found in basic camera lenses and magnifying glasses.

- Plano Convex Lens: Plano refers to the one side of this lens. The other side has an outward curvature. It is frequently seen in optical devices and projectors, where it is intended to focus photons to a precise point.

- Concavo Convex: The faces of this lens are concave and convex. The convex front of this lens has a reduced curvature.

Properties of Convex Lens
- A convex lens’s key characteristic is its ability to converge or focus parallel beams of light. In contrast, diverging lenses, also known as concave lenses, cause parallel rays to diverge.
- Convex lenses possess a real principal focus. When parallel light rays pass through a convex lens, the real focal point appears on the opposite side of the lens from the incident light.
- The positive focal length of a convex lens shows convergence. This positive number is critical in lens formulation calculations.
- Convex lenses provide real images that can be projected onto a screen. These visuals are created by the convergence of light beams.
- Convex lenses produce real images that are inverted and enlarged in comparison to the original item. The degree of enlargement is determined by the object’s position in relation to the focal point.
- A convex lens’ focal point is located on the opposite side of the incident light. The focal length, which is positive, is determined by measuring the distance between the lens’s optical center and the actual focus point.
Application of Convex Lens
- Convex lenses are used in cameras to focus light on the picture sensor or film. This technique guarantees that the final photos are clear and well-defined.
- When magnifying small things, magnifying glasses use virtual, magnified images generated by convex lenses.
- In addition, these same convex lenses can correct hyperopia (also known as farsightedness) by allowing incoming light rays to converge before reaching the eye’s lens.
- By focusing beams of light onto a single point, projectors help to project amplified images onto screens for visual representation.
- Telescopes are optical instruments that use convex lenses to gather and concentrate distant light from celestial bodies and remote landscapes. As a result, we can more accurately observe such phenomena.
Concave Lens
Concave lenses, also known as diverging lenses, are lenses that are thinner in the center than at the borders. It is distinguished by its inwardly curved surfaces. A concave lens diverges or spreads parallel rays of light, as opposed to a convex lens, which converges them.
A concave lens is one that is smaller in the center than on the corners, causing parallel rays of light to diverge as they pass through it.
Types of Concave Lens
- Biconcave Lens: A biconcave lens has two concave curved surfaces. It is symmetrical, with curves facing each other. This lens is smaller in the center than at the borders, and it diverges parallel streams of light.

- Plano Concave Lens: A planoconcave lens has two surfaces: one flat (plano) and one concave. The flat side is usually facing away from the center of the lens. It is a diverging lens, which means that parallel rays of light move out.

- Convexo-concave Lens: Convexo-concave lenses have two distinct surfaces: convex and concave.
The convex side is usually facing outwards. This lens type is a hybrid of a convex and a concave lens, with optical qualities dictated by the radii of curvature of its surfaces. - Double Concave Lenses: The “Double Concave Lens” is compatible with the biconcave lens. It describes a concave lens having two concave surfaces. This lens type is popular because to its divergent features and is thinner in the center than at the borders.
Properties of Concave Lens
- A concave lens’s major feature is its ability to diverge or stretch out parallel rays of light. This differs from converging lenses (convex lenses), which focus parallel rays to a single point.
- Concave lenses are characterized by a virtual principal focus. Parallel light beams passing through a concave lens appear to diverge from a virtual point on the same side as the incident light. For a concave lens, the focus point is virtual.
- Concave lenses have a negative focal length. This reflects the divergent nature of the lens and is an important factor in lens formula calculations.
- Concave lenses produce virtual images.
- Concave lenses provide upright, smaller-than-actual virtual representations of objects. The amount of decrease is determined by the object’s position relative to the focal point.
- A concave lens’ focal point is on the same side as the incident light. The focal length is measured from the lens’s optical center to this virtual focal point and is negative.
Applications of Concave Lens
- Eyeglasses with concave lenses can address visual disorders like myopia. A concave lens helps bring the image into focus on the retina by diverging parallel beams of light before they enter the eye.
- Concave lenses are used in projectors to distribute light rays. This is very handy for projecting broader and larger images on a screen.
- Cameras employ concave lenses to diverge light rays. Concave lenses are employed in certain camera systems to rectify aberrations and distortions.
- Concave lenses in flashlights and automobile headlights provide more even illumination.
- In optical equipment like binoculars and spotting scopes, concave lenses can be used with convex lenses to improve overall performance.
- Galilean telescopes have a concave eyepiece and a convex objective lens. The concave eyepiece improves eye relief and offers a wider field of view.
Difference Between Convex and Concave Lens
| Concave lens | Convex lens | |
| Appearance | Thinner at the center and thicker at the edges | Thicker at the center and thinner at the edges |
| Alternative Name | Diverging Lens | Converging Lens |
| Lens Shape | Curves inward (concave) | Curves outward (convex) |
| Applications | Used in eyeglasses, some telescopes, and door peepholes, Corrects myopia (nearsightedness) | Used in cameras, overhead projectors, microscopes, and magnifying glasses, Corrects hyperopia (farsightedness) |
| Focal Length | Negative focal length | Positive focal length |
| Effect on Light Rays | Causes incident light rays to diverge away from the principal axis | Causes incident light rays to converge towards the principal axis |
| Image Characteristics | Produces an upright, virtual, and smaller image | – Inverted, real, and smaller image when the object is at focus. – Inverted, real, and same-sized image when the object is at 2F – Inverted, real, and larger image when the object is between 2F and F – Image at infinity when the object is at focus – Upright, virtual, and magnified image when the object is on the same side as the lens |
| Light Propagation | Disperses light rays passing through it | Focuses light rays to a point |
| Eyewear Use | Prescribed for nearsightedness | Prescribed for farsightedness |
| Principal Focus | Virtual focus on the same side as the light source | Real focus on the opposite side of the light source |
| Ray Diagram | Displays diverging rays post-lens | Displays converging rays post-lens |
| Magnification | Always forms diminished images | Can form magnified or diminished images depending on object distance |
| Optical Power | Negative optical power | Positive optical power |
| Spherical Aberration | Less susceptible to spherical aberration | More susceptible to spherical aberration unless corrected |
Video Reference
References
- https://byjus.com/physics/difference-between-concave-and-convex-mirror/
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/difference-between-concave-mirror-and-convex-mirror/
- https://keydifferences.com/difference-between-convex-and-concave-mirror.html
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/convex-lens/
- https://www.geeksforgeeks.org/difference-between-concave-convex-lens/
- https://keydifferences.com/difference-between-convex-and-concave-lens.html

