Friedrich Miescher first isolated nucleic acid from the nuclei of leukocytes from discarded surgical bandages and named it nuclein. Nuclein was later discovered to be a combination of basic protein and phosphorous-containing organic acid, now known as nucleic acid. Nucleic are an important class of organic compounds having high molecular weight. They are polymers of nucleotides and play an important role in the development and reproduction of all life forms. There are two types of nucleic acids, i.e., ribonucleic acid (RNA) and deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
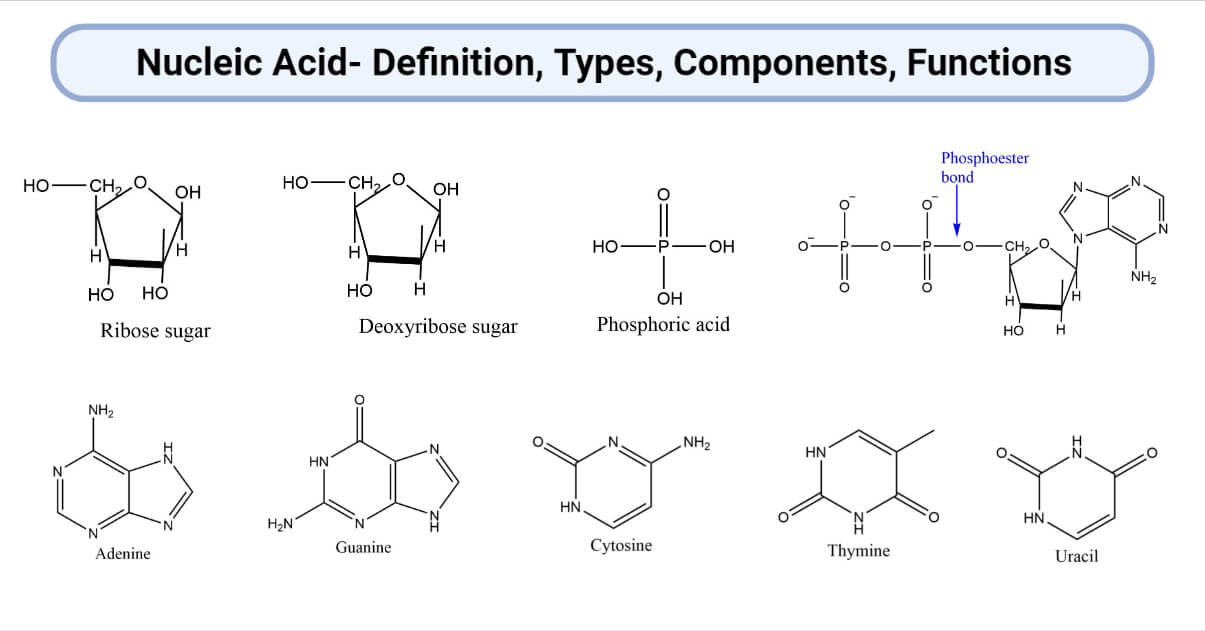
Nucleotides are a monomeric unit of nucleic acids. Nucleic acids are polynucleotides. Nucleotides are phosphate esters of nucleosides and consist of three components.
- Nitrogenous base pair
- A five-carbon sugar
- Phosphoric acid
Interesting Science Videos
Nitrogenous base pair
They are water-insoluble heterocyclic aromatic molecules. Purines and pyrimidines are the two main types of nitrogenous bases commonly present in both DNA and RNA.
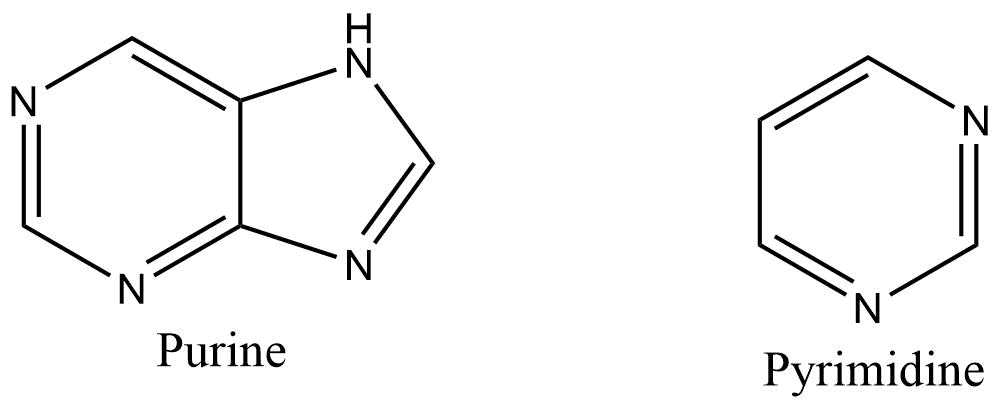
Purines
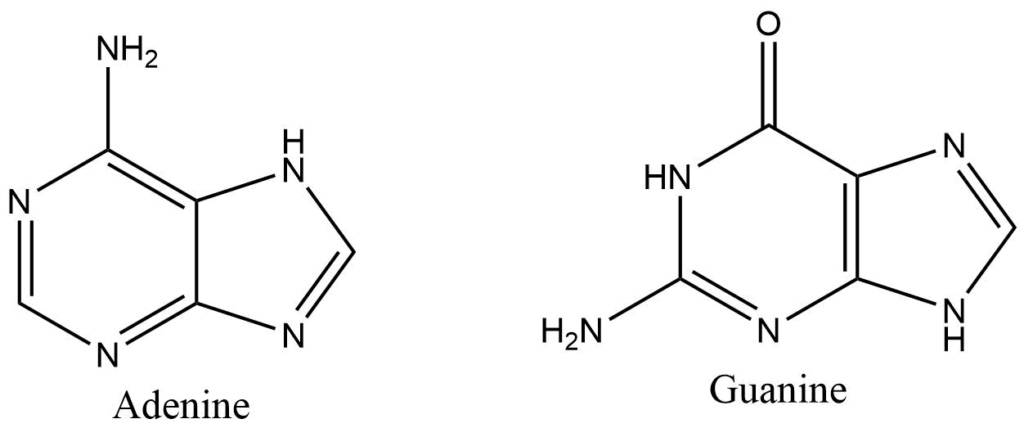
They are heterocyclic aromatic compounds containing six-membered and five-membered nitrogen-containing rings fused together. Adenine and guanine are two common purine bases found in DNA and RNA.
Pyrimidines
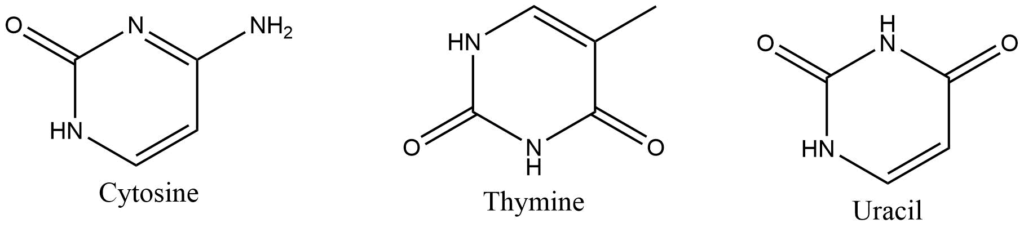
They are six-membered nitrogen-containing rings. Thymine and cytosine are two major pyrimidine bases of DNA while in RNA Uracil and cytosine are present as pyrimidine bases. Uracil is not usually found in DNA. It is a component of RNA.
Sugars
Nucleic acids generally consist of ribose and deoxyribose sugar. All known sugars in nucleic acid have a D-stereoisomeric configuration.
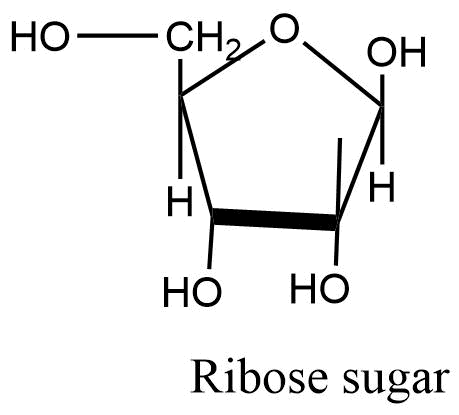
Ribose sugar
Ribose sugar is 5-carbon sugar with a hydroxyl group i.e. -OH group on each carbon atom. RNA consists of ribose sgar.
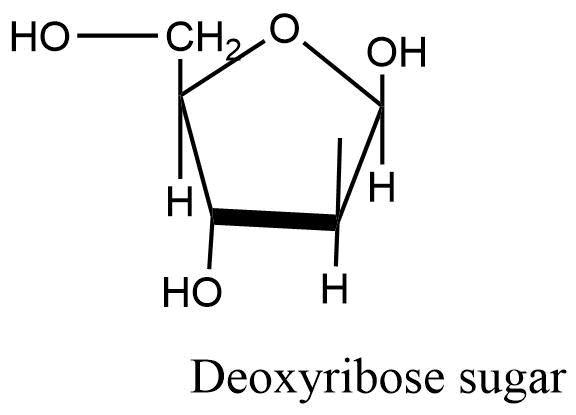
Deoxyribose sugar
It is also a 5-carbon sugar in which the hydroxyl group of ribose sugar is replaced by hydrogen. DNA consists of deoxyribose sugar.
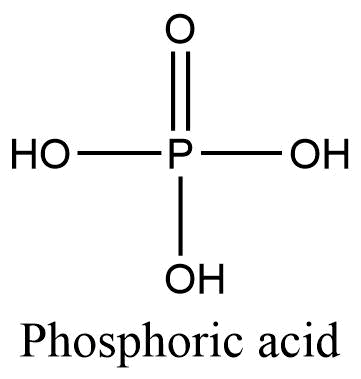
Phosphoric acid
Phosphoric acid is an important component of nucleic acid. In nucleotides, two nucleosides are joined together by phosphodiester bonds.
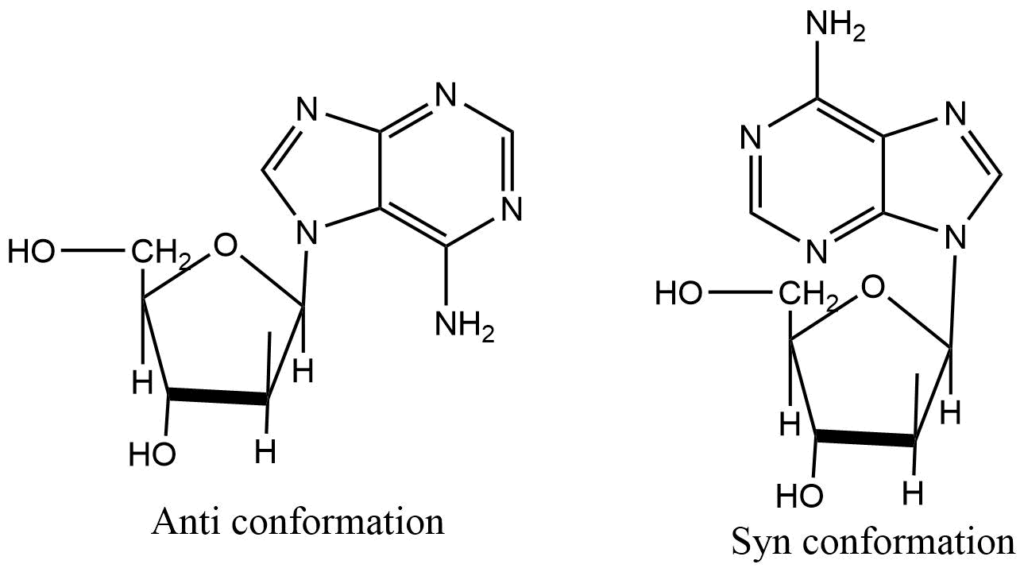
Nucleosides
Nitrogenous base pair and sugar units are joined together by a glycosidic bond to form a nucleoside. The base is free to rotate around the glycosidic bonds, so two different conformers of the base are possible, namely syn and anti. Because of steric hindrance between O-2 and C-5′ in syn conformation, pyrimidines tend to adopt anti-conformation, whereas purines can have both syn and anti-forms.
Nucleotides
Nucleotides are phosphoric acid esters of nucleosides. They are monomeric units of RNA and DNA.
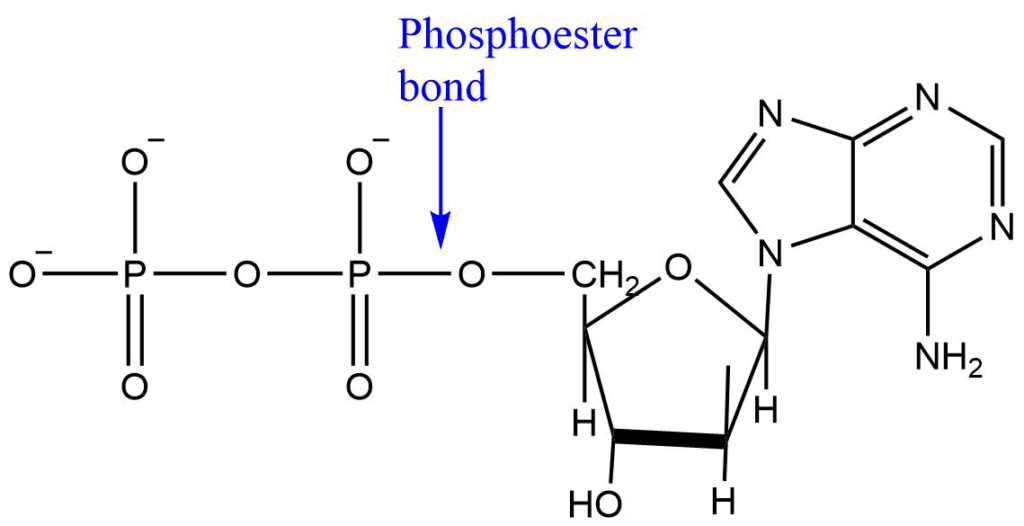
Nucleotides are also required for other numerous functions within the cells. They are :
- They act as intermediates in many biosynthetic reactions.
- It acts as a precursor for several coenzymes like NAD+, NADP+, and FAD.
- They are involved in the formation of ATP, and GTP.
- They serve as precursors for secondary messengers like cyclic AMP.
RNA (Ribonucleic acid)
Ribonucleic acid is a high molecular weight organic compound that plays an important role in cellular protein synthesis. It acts as genetic material in some viruses. RNA consists of ribonucleosides (i.e., ribose sugar and nitrogenous bases are linked together by a glycosidic bond) attached by phosphodiester bonds. Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, and Uracil are the main nitrogenous bases present in RNA.RNA generally consists of a single strand. There are three commonly studied RNAs. They are
- Messenger RNA (mRNA)
- Transfer RNA (tRNA)
- Ribosomal RNA (rRNA)
DNA (Deoxyribonucleic acid)
Deoxyribonucleic acid is a high molecular weight organic compound that acts as genetic material. It is used to store the genetic information of living organisms. It comprises deoxyribose sugar, nitrogenous base pair, and phosphoric acid. Adenine, Guanine, Cytosine, and Thymine are the main nitrogenous base pairs present in DNA. DNA has a double-strand helical structure. Two strands in DNA are complementary to each other.
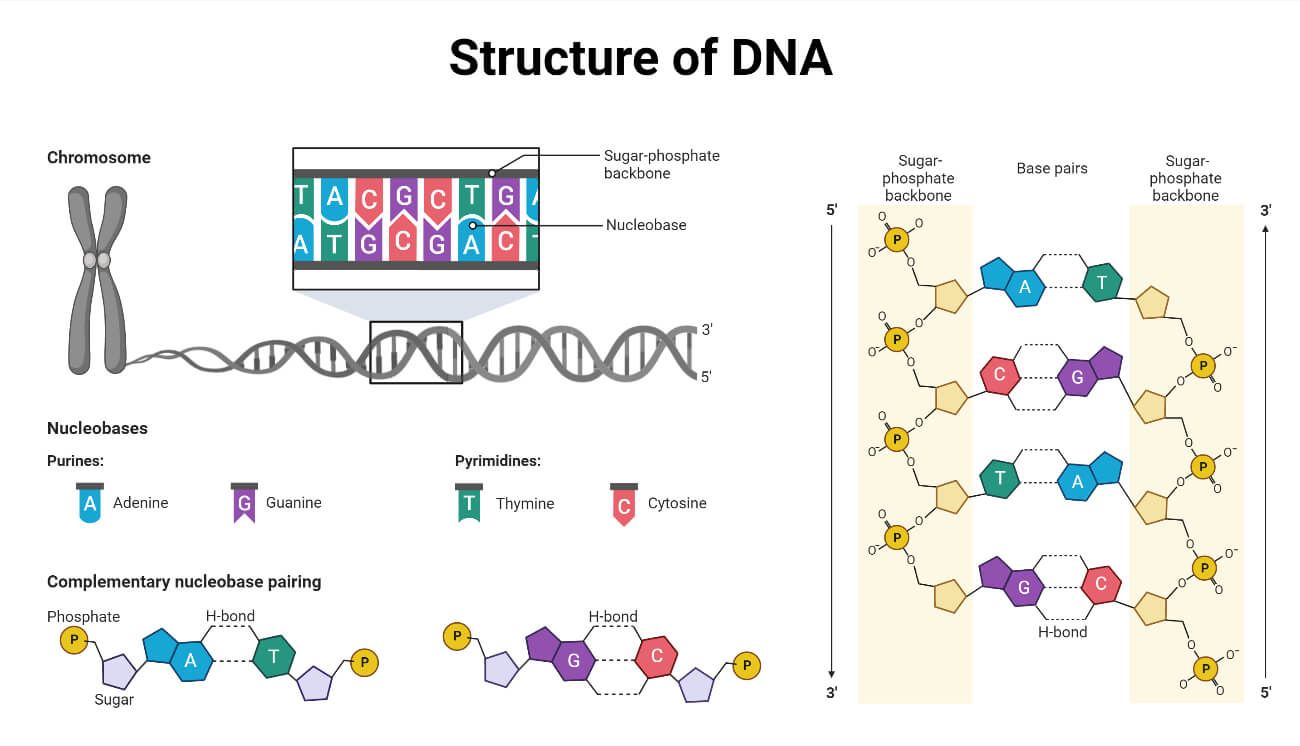
Functions of Nucleic acids
- DNA acts as genetic material in all living organisms except viruses.
- Nucleic acids play an important role in transforming genetic information from one generation to another.
- RNA involves in protein synthesis.
- Some RNA acts as enzymes.
- They carry chemical energy in cells in the form of ATP and GTP.
- They are the components of coenzymes like NAD+ and NADP+.
- Some Nucleotides function as regulatory molecules.
References
- Satyanarayana, U., & Chakrapani, U. (2013). Biochemistry. New Delhi: Elsevier Health Sciences APAC.
- https://byjus.com/chemistry/function-nucleic-acids/
- https://www.genome.gov/genetics-glossary/Nucleic-Acids
- https://biologydictionary.net/nucleic-acid/
- https://www.britannica.com/science/nucleic-acid
- https://www.vedantu.com/chemistry/function-of-nucleic-acids
- https://www.aakash.ac.in/important-concepts/chemistry/functions-of-nucleic-acids
