Several sodas, packaged foods, and personal care goods have sodium benzoate added as a preservative to extend shelf life. The Food and Drug Administration approved sodium benzoate as the first food preservative. If it is ingested in doses that are less than 5 mg/kg of body weight per day, it is regarded as safe for human health. It establishes the daily dosage of a particular substance that a person can eat without endangering their health.
Interesting Science Videos
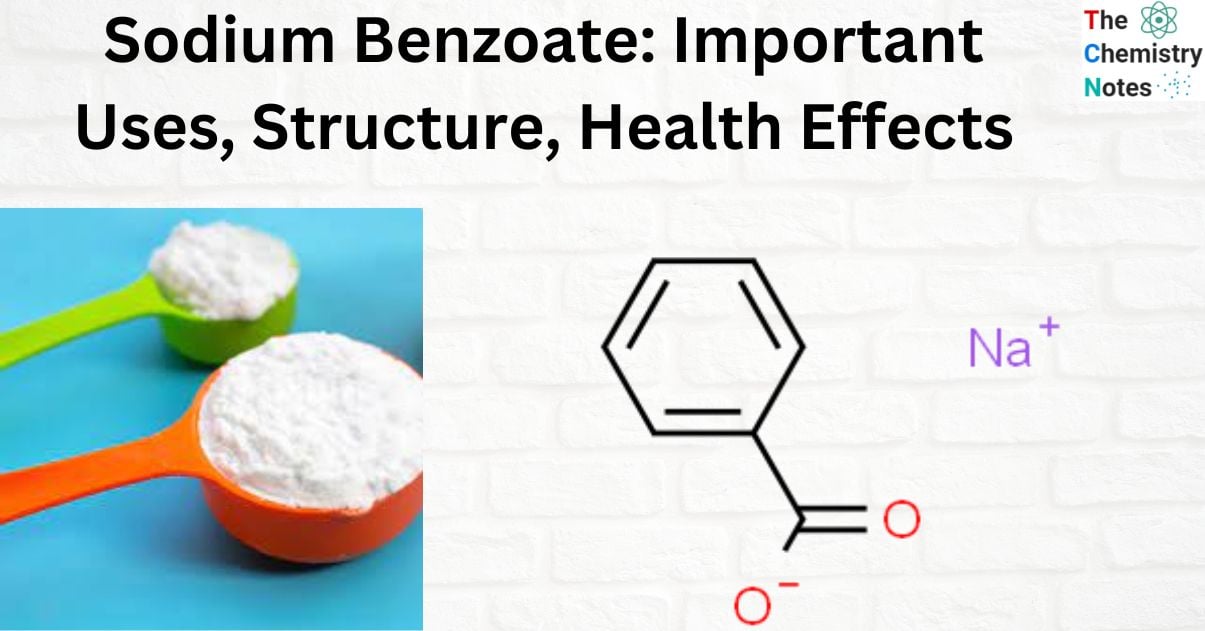
What is Sodium Benzoate?
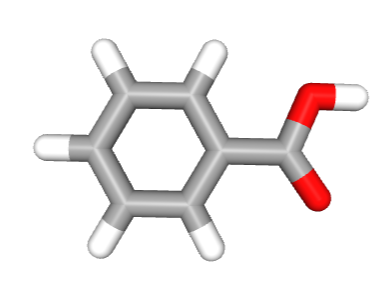
Sodium benzoate is a salt of benzoic acid that is well soluble in water, tasteless, and odorless and is used as a preservative in food at tightly controlled dosages due to its antifungal and antibacterial effects. It prevents bacteria, yeast, and mold from growing.
Food preservatives are used to preserve food safety and to prevent quality loss caused by microbiological, physical-chemical, or enzymatic processes.
It is an organic sodium salt formed by replacing the proton in the carboxy group of benzoic acid with a sodium ion. It functions as an antibacterial food preservative, a drug allergen, an arachidonate 15-lipoxygenase (EC 1.13.11.33) inhibitor, a triacylglycerol lipase (EC 3.1.1.3) inhibitor, an algal metabolite, a human xenobiotic metabolite, and a plant metabolite. It contains benzyl benzoate.
It is used as a preservative to prevent food from molding. It helps keep our products shelf-stable for at least two years from the date of purchase and is used in concentrations of less than 0.5% by volume.
While considered safe, scientists have shown that negative side effects occur when it’s mixed with ascorbic acid (vitamin C). Their studies indicate that it then turns into benzene, a known carcinogen that may cause cancer.
Structure
Uses of Sodium Benzoate
- This was the first food preservative approved by the FDA and is still frequently used today. It is designated as Generally Recognized As Safe (GRAS), which means that experts believe it is safe when taken as directed.
- In food,it suppresses the growth of potentially dangerous bacteria, mold, and other germs, preventing spoiling. It works very well with acidic foods.
- Numerous studies demonstrate that sodium benzoate, especially in high concentrations, can be harmful to one’s health through a variety of processes. Some research, however, shows that this chemical has positive qualities and may be employed in the development of therapeutic strategies for certain disorders via the same or comparable modes of action.
- It is found in a variety of foods, including soda, bottled lemon juice, pickles, jellies, salad dressing, soy sauce, and other condiments.
- Because of its capacity to bind amino acids, sodium benzoate is utilized to treat urea cycle problems.
- Hyperammonemia is treated with sodium benzoate and phenylbutyrate.
- Sodium benzoate, coupled with caffeine, is used to treat post-dural puncture headaches, respiratory depression caused by opioid overdosage, and vascular headaches.
- Because of its qualities, sodium benzoate is used to preserve acidic food products such fruit pulp and purees, jams, pickles, pickled herring and mackerel, margarine, olives, beer, fruit yogurts, canned vegetables, and salads. Sodium benzoate is commonly found in carbonated beverages, sauces, mayonnaises, margarine, tomato paste, and fruit preserves. In turn, it can be found in cinnamon, mushrooms, cranberries, blueberries, and cloves in their natural form. As a result, sodium benzoate is recognized as a substance with a high level of safety.
Sodium Benzoate and Health Effects
It is considered safe and can be used as an antibacterial agent and flavoring agent in food at a maximum concentration of 0.1%. The FDA considers 5 ppb to be the maximum acceptable quantity of sodium benzoate in drinking water. Almost all beverage products fall inside this range and will not harm our health. Several studies also show that sodium benzoate has considerable therapeutic potential, particularly for neurodegenerative illnesses, ASD, schizophrenia, MDD, and pain alleviation, via numerous mechanisms.
Negative Effects
Many buyers are worried about preservatives like sodium benzoate. It is often assumed that this is harmful to your health and has a number of adverse effects.
- When it reacts with vitamin C, as it does in some soft drinks and other liquids, and is exposed to high temperatures or light, the cancer-causing chemical benzene can occur.
- Although it is generally considered safe during pregnancy, it is best to discuss it with your doctor before taking items containing sodium benzoate.
- A limited number of persons may be allergic to preservatives and develop the following allergy symptoms. Epidemiologically significant (itching and swelling), Urticaria from perioral touch (skin irritation like rosacea), and Pruritus (an painful urge to scratch) (an uncomfortable urge to scratch)
- ADHD (Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder): A study of college students found a relationship between ADHD and a higher intake of sodium benzoate in beverages. In other research, chemical addition has also been associated to ADHD in youngsters.
- Leptin, a hormone that suppresses appetite, was released less often in a test-tube investigation using mice fat cells after sodium benzoate exposure. The reduction was 49-70%, according to the exposure.
- Oxidative stress: Research conducted in test tubes indicates that more free radicals are produced at greater sodium benzoate concentrations. Free radicals can harm your cells and raise your chance of developing chronic diseases.
Positive Effects
In higher doses, sodium benzoate may aid in the treatment of some medical disorders.
- The chemical lowers excessive blood levels of the waste product ammonia, which is common in persons with liver disease or genetic urea cycle abnormalities, which impede ammonia elimination through urine.
- Additionally, scientists have uncovered mechanisms through which sodium benzoate may have therapeutic benefits, such as binding undesirable chemicals or influencing the activity of specific enzymes that increase or decrease the levels of other substances.
- Other potential medicinal uses of sodium benzoate that are being researched include Schizophrenia, Multiple sclerosis (MS), Maple syrup urine disease, Depression.
- Sodium benzoate is a preservative widely found in cosmetics and personal care goods such as hair products, baby wipes, toothpaste, and mouthwash
- It also has industrial use. One of its most important applications is to prevent corrosion, such as in car engine coolants
- Furthermore, it can be used as a stabilizer in picture processing and to increase the strength of various plastics.
References
- “Benzoic acid and its derivatives as naturally occurring compounds in foods and as additives: Uses, exposure, and controversy”. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition.
- Sodium Benzoate—Harmfulness and Potential Use in Therapies for Disorders Related to the Nervous System: A Review. doi: 10.3390/nu14071497
- “Sodium benzoate”. PubChem. National Library of Medicine
- https://www.healthline.com/nutrition/sodium-benzoate#benefits
- https://www.webmd.com/diet/what-to-know-about-sodium-benzoate
