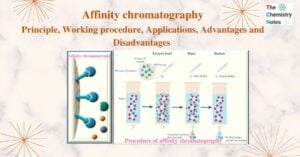
Affinity chromatography: Principle, Procedure, Applications, Advantage
Affinity chromatography is a liquid chromatography technique that employs biospecific interactions to separate compounds. The molecule that needs to be purified is selectively and irreversibly adsorbed to a certain ligand. … Read more