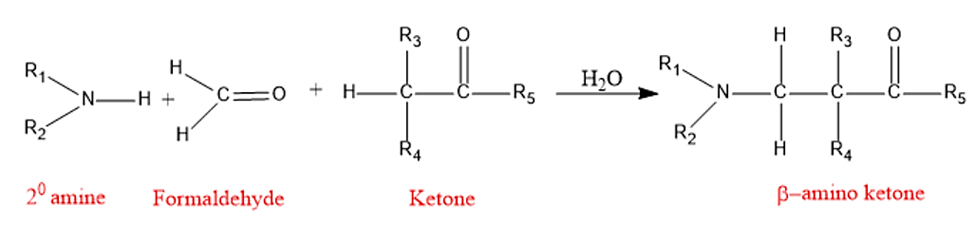
The Mannich reaction is a fundamental and significant C-C bond formation process in organic synthesis. The Mannich reaction is an organic reaction that is used to create a β-amino carbonyl molecule from a primary or secondary amine and two carbonyl compounds (one non-enolizable and one enolizable).
Mannich reaction was named after Carl Ulrich Franz Mannich, a German chemist who discovered it in 1912.
Interesting Science Videos
What is Mannich Reaction?
The Mannich reaction is an amino alkylation reaction that involves the condensation of an enolizable carbonyl compound (α-CH acidic compound) with a nonenolizable aldehyde (like formaldehyde) and ammonia; or a primary or secondary amine to yield a β-aminocarbonyl compound, also known as Mannich base.
The Mannich reaction is an organic reaction that consists of a formaldehyde and ammonia or any primary or secondary amine amino alkylation of an acidic proton next to a carbonyl functional group to form β-amino-carbonyl compound. Aldimines form between amines and aldehydes, therefore reactions between them and α-methylene carbonyls are also regarded as Mannich reactions.
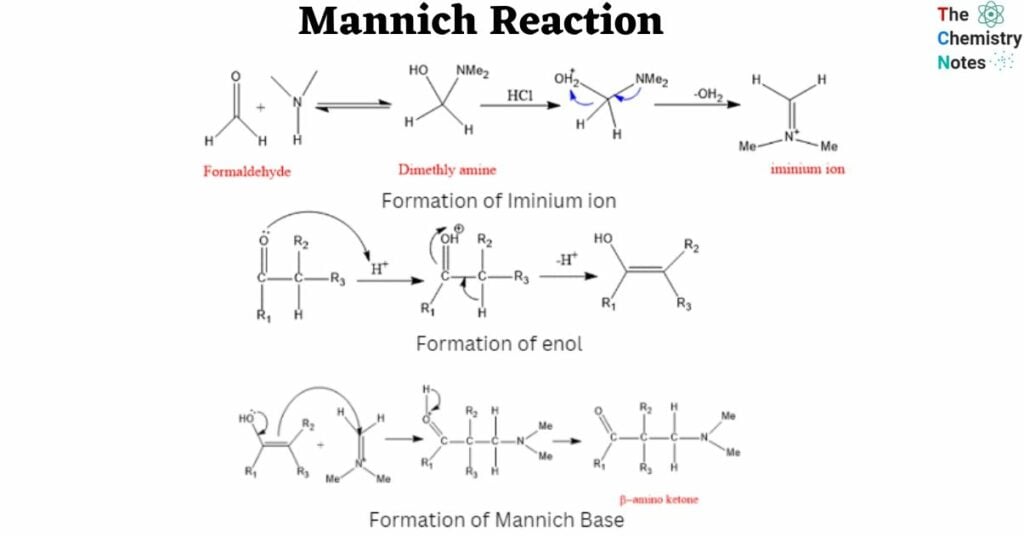
Mechanism of Mannich Reaction
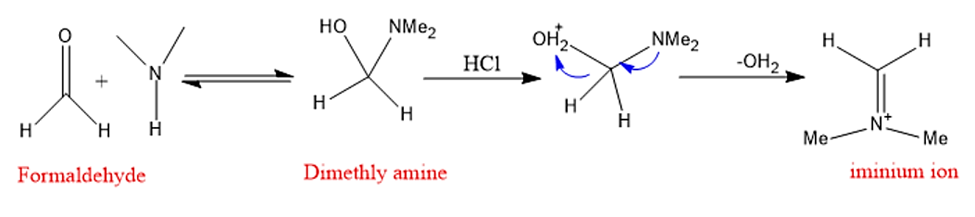
Step 1: In the first stage, formaldehyde combines with amine, which is then deprotonated and dehydrated to create iminium ion.
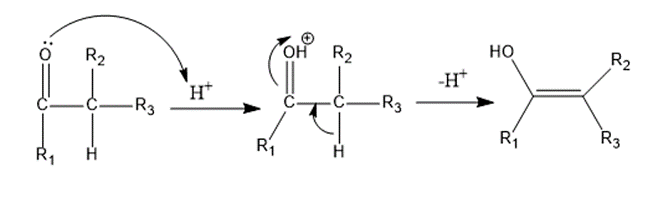
Step 2: In the second step, the carbonyl molecule (ketone in this case) with an α-hydrogen is protonated and subsequently deprotonated to undergo tautomerization and generate an enol form.
Step 3: The required product, β-amino carbonyl compound, is synthesized after deprotonation of the compound produced by this enol, the nucleophile, attacking the iminium ion.
![Formation of Mannich Base [Mannich reaction]](https://scienceinfo.com/wp-content/uploads/2023/08/image-157.png)
Applications of Mannich Reaction
- This reaction is used for the preparation of alkyl amines which are used for making agrochemicals such as pesticides.
- It is used for the synthesis of organic compounds such as nucleotides and peptides.
- Mannich bases are widely used in the pharma industry for the synthesis of numerous pharmaceutical drugs such as fluoxetine, which is a strong antidepressant.
- Catalysts and polymers are made by the Mannich reaction.
- A lot of antibiotics are Mannich bases. Tetracycline is an antibiotic whose Mannich base is rolitetracycline.
- Using Mannich Reaction non-polar hydrocarbons can be converted into soaps and detergents.
- Cleaning solutions, vehicle fuel treatment, and epoxy coatings are just a few of the applications. Substituted long-chain alkyl ethers are converted to polyether amines by a variety of techniques.
- Tropinone is synthesized by the Robinson-Schopf process, which includes the Mannich reaction. Tropinone is produced by treating succindialdehyde (butanedial) with methylamine and 3-oxoglutaric acid (3-oxopentanedioic acid).
Video on Mannich Reaction
References
- Morrison R. T. & Boyd R. N. (1983). Organic chemistry (4th ed.). Allyn and Bacon.
- Smith M. & March J. (2001). March’s Advanced Organic Chemistry: Reactions Mechanisms and Structure (5th ed.). Wiley.
- Ghosh, S.K., Advanced General Organic Chemistry, Second Edition, New Central Book Agency Pvt. Ltd., Kolkatta, 2007.
- https://www.organic-chemistry.org/namedreactions/mannich-reaction.shtm
- https://byjus.com/chemistry/mannich-reaction-mechanism/

