You may learn a lot about an element’s characteristics from its position in the periodic table as well as from its arrangement. This periodic table with charges is a helpful means to keep a record of the most common oxidation numbers for each element. An atom’s charge is determined by the difference between its protons (positive charge) and electrons (negative charge). Each element has a distinct number of protons in the center of its atom, or nucleus. However, as atoms frequently lose or receive electrons, determining their charge can be difficult.
Interesting Science Videos
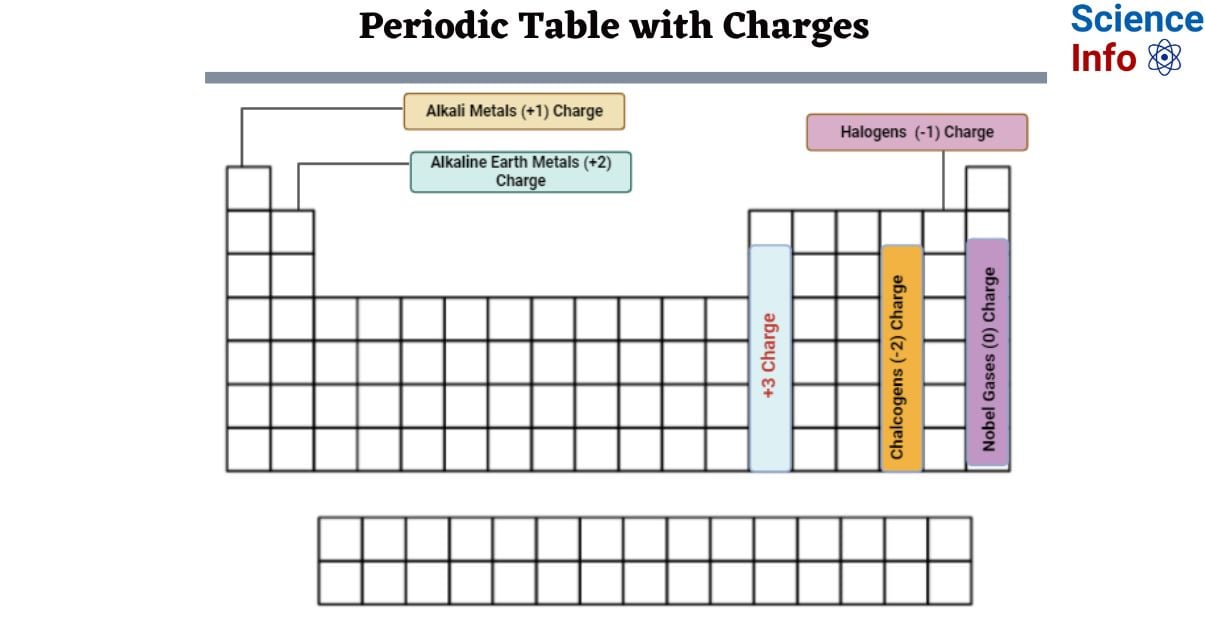
Elements in Periodic Table with Charges
This is a chart of the most common charges for atoms in chemical elements. This chart can help you forecast whether or not an atom will bond with another atom. The charge of an atom is determined by its valence electrons or oxidation state. An element’s outer electron shell is most stable when it is entirely or partially filled. The most prevalent charges aim to maximize the atom’s stability. Other charges may apply, however.
For example, hydrogen might have a charge of zero or, less typically, -1. Although noble gas atoms usually always have a zero charge, they do create compounds in which they can gain or lose electrons and have a charge.
| Number | Element | Charge |
| 1 | hydrogen | 1+ |
| 2 | helium | 0 |
| 3 | lithium | 1+ |
| 4 | beryllium | 2+ |
| 5 | boron | 3-, 3+ |
| 6 | carbon | 4+ |
| 7 | nitrogen | 3- |
| 8 | oxygen | 2- |
| 9 | fluorine | 1- |
| 10 | neon | 0 |
| 11 | sodium | 1+ |
| 12 | magnesium | 2+ |
| 13 | aluminum | 3+ |
| 14 | silicon | 4+, 4- |
| 15 | phosphorus | 5+, 3+, 3- |
| 16 | sulfur | 2-, 2+, 4+, 6+ |
| 17 | chlorine | 1- |
| 18 | argon | 0 |
| 19 | potassium | 1+ |
| 20 | calcium | 2+ |
| 21 | scandium | 3+ |
| 22 | titanium | 4+, 3+ |
| 23 | vanadium | 2+, 3+, 4+, 5+ |
| 24 | chromium | 2+, 3+, 6+ |
| 25 | manganese | 2+, 4+, 7+ |
| 26 | iron | 2+, 3+ |
| 27 | cobalt | 2+, 3+ |
| 28 | nickel | 2+ |
| 29 | copper | 1+, 2+ |
| 30 | zinc | 2+ |
| 31 | gallium | 3+ |
| 32 | germanium | 4-, 2+, 4+ |
| 33 | arsenic | 3-, 3+, 5+ |
| 34 | selenium | 2-, 4+, 6+ |
| 35 | bromine | 1-, 1+, 5+ |
| 36 | krypton | 0 |
| 37 | rubidium | 1+ |
| 38 | strontium | 2+ |
| 39 | yttrium | 3+ |
| 40 | zirconium | 4+ |
| 41 | niobium | 3+, 5+ |
| 42 | molybdenum | 3+, 6+ |
| 43 | technetium | 6+ |
| 44 | ruthenium | 3+, 4+, 8+ |
| 45 | rhodium | 4+ |
| 46 | palladium | 2+, 4+ |
| 47 | silver | 1+ |
| 48 | cadmium | 2+ |
| 49 | indium | 3+ |
| 50 | tin | 2+, 4+ |
| 51 | antimony | 3-, 3+, 5+ |
| 52 | tellurium | 2-, 4+, 6+ |
| 53 | iodine | 1- |
| 54 | xenon | 0 |
| 55 | cesium | 1+ |
| 56 | barium | 2+ |
| 57 | lanthanum | 3+ |
| 58 | cerium | 3+, 4+ |
| 59 | praseodymium | 3+ |
| 60 | neodymium | 3+, 4+ |
| 61 | promethium | 3+ |
| 62 | samarium | 3+ |
| 63 | europium | 3+ |
| 64 | gadolinium | 3+ |
| 65 | terbium | 3+, 4+ |
| 66 | dysprosium | 3+ |
| 67 | holmium | 3+ |
| 68 | erbium | 3+ |
| 69 | thulium | 3+ |
| 70 | ytterbium | 3+ |
| 71 | lutetium | 3+ |
| 72 | hafnium | 4+ |
| 73 | tantalum | 5+ |
| 74 | tungsten | 6+ |
| 75 | rhenium | 2+, 4+, 6+, 7+ |
| 76 | osmium | 3+, 4+, 6+, 8+ |
| 77 | iridium | 3+, 4+, 6+ |
| 78 | platinum | 2+, 4+, 6+ |
| 79 | gold | 1+, 2+, 3+ |
| 80 | mercury | 1+, 2+ |
| 81 | thallium | 1+, 3+ |
| 82 | lead | 2+, 4+ |
| 83 | bismuth | 3+ |
| 84 | polonium | 2+, 4+ |
| 85 | astatine | ? |
| 86 | radon | 0 |
| 87 | francium | – |
| 88 | radium | 2+ |
| 89 | actinium | 3+ |
| 90 | thorium | 4+ |
| 91 | protactinium | 5+ |
| 92 | uranium | 3+, 4+, 6+ |
| 93 | neptunium | 3+, 4+, 5+ |
| 94 | plutonium | 3+, 4+, 5+ |
| 95 | americium | 3+ |
| 96 | curium | 3+ |
| 97 | berkelium | 3+ |
| 98 | californium | 3+ |
| 99 | einsteinium | 3+ |
| 100 | fermium | 3+ |
| 101 | mendelevium | 3+ |
| 102 | nobelium | 3+ |
| 103 | lawrencium | 3+ |
Video on Periodic Table with Charges
References
- https://chemistrytalk.org/periodic-table-with-charges/
- Helmenstine, Anne Marie, Ph.D. “Element Charges Chart.” ThoughtCo, Jul. 18, 2022, thoughtco.com/element-charges-chart-603986.
- https://sciencenotes.org/periodic-table-with-charges-pdf/

