Acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) is an impact-resistant engineering thermoplastic composed of acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene polymers. ABS is a popular thermoplastic polymer used in injection molding. The polymerization of acrylonitrile and polystyrene monomers with butadiene rubber yields acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS). This blending is often performed using an emulsification technique.

ABS is a popular choice among plastic manufacturers because of its durability, structural stability, and good corrosion, impact, chemical, and wear resistance.
Interesting Science Videos
What is ABS Plastic?
ABS plastic, or Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene, is an opaque thermoplastic amorphous polymer that is widely utilized in a variety of manufacturing applications. ABS plastic is a terpolymer composed of three monomers: acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene.
Acrylonitrile improves chemical resistance, fatigue resistance, hardness, stiffness, and heat deflection temperature. Butadiene increases toughness and ductility at low temperatures, whereas styrene improves surface properties, hardness, rigidity, and processability.
ABS: What does it stand for?
The acronym ABS stands for Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene. It’s an impact-resistant engineering thermoplastic. It contains an amorphous polymer. ABS consists of three monomers: acrylonitrile, butadiene, and styrene.
Acrylonitrile is a synthetic monomer. It is made from propylene and ammonia. This component contributes to the chemical resistance and heat stability of ABS.
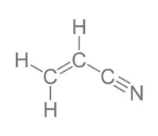
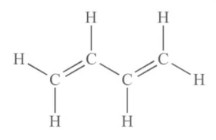
Butadiene is a byproduct of the ethylene manufacturing process at steam cracker plants. This component provides toughness and impact strength to the ABS polymer.
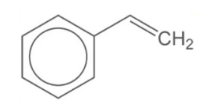
Styrene is produced by the dehydrogenation of ethylbenzene. It adds stiffness and processability to ABS plastic.
How to Manufacture ABS Plastic
ABS materials are commonly manufactured using the following procedures.
- Injection molding
- CNC Machining
- 3D printing
ABS Injection Molding
ABS injection molding is comparable to thermoplastic injection molding. The ABS resin pellets are fed into a hopper first. The pellets are then melted under tremendous pressure. As the pellets melt, they are injected into the mold. After cooling and solidifying, the final step is to inject the item from the mold. The operation is repeated once the portion has been injected.
Advantages of ABS Injection Molding
- It produces less waste. It is an environmentally favorable method because it generates less garbage.
- It produces high-quality, large-volume components efficiently.
- It allows for complex and multi-featured parts, including metal inserts.
- It improves mechanical strength and durability for manufactured products. Because of the enhanced mechanical power, they are more durable.
- Injection molding is an automated process, which requires less human interaction. Because the process requires less human interaction, the labor cost is low, lowering the cost of the components.
Disadvantages of ABS Injection Molding
- ABS injection molding has a high initial investment cost
- This can lead to material burning if done incorrectly. It could be the result of trapped gases exerting high pressure, culminating in ignite. It could eventually cause the material to burn.
- ABS injection molding produces products at a reasonable cost due to automation. However, tooling costs are high.
ABS CNC Machining
ABS plastic is the most common material used for CNC machining. The entire operation is controlled by specialized computer programs. It employs numerous CNC machines, including lathes, grinders, routers, and mills. Multiple machine tools are used to cut and remove material from a workpiece.
During the process, the material is subtracted from the workpiece using the information provided by the computer programs. Thus, the raw material is converted into a desirable finished product.
Advantages of CNC Machining
- ABS CNC machining produces more accurate products due to computer-controlled manufacturing processes.
- Accurate manufacturing leads to longer-lasting parts. It automatically ensures that components work properly over time.
- This is the quickest approach to creating prototypes of ABS plastic. Because of the rapid manufacturing of prototypes, it aids in speedy mass production.
- CNC machining is a computer-controlled procedure for creating parts with complex geometries. It provides greater accuracy than traditional manufacturing methods since it is computer-controlled.
- ABS CNC machining produces ABS items according to the instructions provided.
- As a result of this procedure, items with complex geometries are manufactured with increased accuracy and precision.
- This process ensures a smoother surface finish. You do not need to use any post-processing processes to get a suitable surface finish, which can increase prices.
- ABS CNC machining is more cost-effective than ABS injection molding. This cost-effectiveness stems mostly from the fact that ABS CNC machining eliminates the need for expensive molds, which are required in the injection molding procedure.
Disadvantages of ABS CNC Machining
- The biggest downside is that it can produce excessive waste.
- The cost of CNC machining equipment is expensive. As a result, producing ABS parts requires a significant financial investment.
ABS 3D Printing
ABS components are largely created using 3D printing technology. Typically, FFF or FDM printers are used for this. The printer generates lengthy, filamentous ABS wounds around the spool. The filamentous ABS is then fed through the extruder or extrusion head. They are cooked till they turn into a liquid. After liquifying, they are placed as layers on the printing platform, making it the simplest method for producing a large number of ABS components.
Advantages of ABS 3D Printing
- FDM technology has significantly lowered the cost of 3D printing. ABS 3D printing can also result in inexpensive production costs.
- ABS filaments used in 3D printing have superior mechanical qualities, including impact resistance, flexibility, and strength. As a result, it makes an outstanding industrial-grade material.
- ABS 3D printing has the advantage of being easy to process. ABS may be simply processed using glue and acetone components.
- ABS 3D printing can produce high-quality models with smooth finishes when used correctly. Printing overhangs is significantly easier with this material. Furthermore, it provides a beautiful, smooth finish to the final model result.
- ABS material is noted for its exceptional mechanical properties, including increased hardness and strength. Furthermore, it is very resistant to various chemicals and heat. When compared to other 3D printing materials, it performs better under pressure, high temperatures, and stress situations.
Disadvantages of ABS 3D Printing
- ABS 3D printing may necessitate advanced capabilities in 3D printers to ensure quality results. It requires powerful 3D printers, which can be costly and difficult to obtain.
- One major downside of ABS 3D printing is the generation of unpleasant odors. During the procedure, an unpleasant odor is produced and is deemed uncomfortable. Evidence also indicates that the fumes produced by burning plastic include harmful chemicals.
- ABS might crack or curl during printing. Cracks typically form during the cooling of the parts and can eventually cause the printer to fail by interfering with its performance.
- Warping is a typical downside. The ABS begins to shrink during the printing process when it cools. After shrinking, it begins peeling off and rising from its corners, a process known as warping. It may have an impact on how printers work.
Properties of ABS Plastic
Tensile strength: ABS has high tensile strength, making it useful for a variety of applications. ABS’s tensile strength is defined as its capacity to endure pulling forces without failure or irreversible deformation. ABS has tensile strength ranging from 30 to 60 megapascals (MPa), which maintains its strength and load-bearing capabilities. ABS is a great option for applications where components must withstand mechanical stress and forces, such as consumer items, automotive parts, and structural components, because of its high tensile strength
UV-Ressistance: ABS is moderately resistant to ultraviolet (UV) rays, however, it is not UV stable. Specialized formulas or UV stabilizer-containing coatings can be utilized to improve ABS UV resistance. This helps to reduce color fading and surface damage when ABS is exposed to prolonged sunlight or outdoor environments. ABS materials with enhanced UV protection are frequently utilized in outdoor applications, including vehicle exterior parts, garden furniture, and outdoor signage.
Modulus of elasticity: The modulus of elasticity, commonly known as Young’s modulus, is an important mechanical property that determines a material’s stiffness and capacity to deform when stressed. ABS has a lower modulus of elasticity than other technical polymers, often ranging between 1.9 and 2.5 gigapascals (GPa). This feature gives ABS flexibility and impact resistance, allowing it to absorb shocks and vibrations.
Chemical resistance: ABS materials are highly resistant to a variety of substances, including acids, alkalis, and solvents. This feature guarantees that ABS components retain their integrity and performance in areas where chemical exposure is likely. ABS is widely utilized in the automotive, electrical, and medical industries, where it confronts a variety of chemicals and compounds.
Shrink rate: ABS materials shrink relatively quickly during the cooling process after manufacturing. Shrink rate is the percentage drop in size that occurs as the molten ABS cools and hardens. ABS shrink rates typically vary from 0.4% to 0.8%. Manufacturers must account for shrinkage during the design and manufacturing stages to maintain dimensional correctness and avoid warping or distortion.
Mechanical and Electrical Properties of ABS Plastic
| Property | Value |
| Mechanical Properties | |
| Heat deflection temperature | 98°C (208°F) at 0.46 MPa (66 PSI) |
| Toughness (Notched Izod Impact) | 200 – 215 J/m |
| Elongation at yield | 1.7-6% |
| Shrink rate | 0.5-0.7% |
| Flexural Strength | 74 MPa (10800 PSI) |
| Hardness (Shore D) | 100 |
| Elongation at break | 10-50% |
| Specific gravity | 1.06 |
| Tensile strength | 46 MPa (6600 PSI) |
| Electrical Properties | |
| Volume Resistivity | 14 – 16 x 1015 Ohm.cm |
| Arc resistance | 60-120 sec |
| Dielectric Constant | 2.7-3.2 |
| Dissipation factor | 50 – 190 x 10-4 |
| Dielectric Strength | 15.7 – 34 kV/mm |
Application of ABS Plastic
Electronics: ABS plastic is widely utilized in the manufacture of consumer electronics such as computer keyboards, computer mice, remote controls, phone casings, and audio/video equipment housings. Its impact resistance, adaptability, and electrical insulation make it ideal for various applications.
Household appliances: Vacuum cleaners, blenders, coffee makers, toasters, and kitchen utensils are made from ABS plastic. Its strength, chemical resistance, and ease of processing make it appropriate for various applications.
Medical devices: This material is utilized in the medical field to create a variety of devices and equipment. This comprises medical instrument casings, laboratory equipment, disposable syringes, and medical device components. ABS plastic is ideal for medical applications due to its durability, chemical resistance, and simplicity of sterilizing.
Sports Equipment: ABS plastic is used to manufacture sports and recreational equipment such as helmets, protective clothing, sporting equipment, skateboards, and bicycles. Its impact resistance and ability to tolerate outdoor environments make it ideal for these applications.
Automotive parts: This material is commonly utilized in the automotive industry for a variety of interior and external components. Dashboards, instrument panels, door panels, trim, grilles, mirror housings, and interior console components are some examples. ABS plastic’s strength, impact resistance, and surface polish make it ideal for automotive applications.
Toys and games: ABS plastic is a popular material for making toys and games because of its durability, impact resistance, and ability to be molded into complicated patterns.
Advantages of ABS Plastic
ABS has many advantages as a general-purpose engineering material. Here are some of the advantages of ABS plastic:
- Impact resistance: ABS plastic is well-known for its high impact resistance, making it ideal for applications that demand durability and strength.
- Strength and Stiffness: ABS has excellent mechanical qualities, including high strength and stiffness. Its capacity to bear loads and strains makes it appropriate for structural components.
- Versatility: ABS plastic is a manufacturable material that can be easily molded and sculpted using a variety of services such as injection molding, machining, and 3D printing.
- Chemical resistance: The material is resistant to a wide range of chemicals, such as acids, alkalis, and solvents.
- Electrical Insulation: ABS has good electrical insulation qualities, hence it is commonly found in electrical and electronic components, housings, and enclosures.
- Surface finish: ABS plastic can be easily polished and post-processed to create a smooth and visually pleasing surface.
Disadvantages of ABS Plastic
ABS material has some drawbacks, which are outlined below:
- ABS has a low melting point when compared to other polymers, making it unsuitable for high-heat applications.
- ABS is highly susceptible to fatigue stress, solvents/greases, and UV radiation exposure.
- When heated, ABS emits considerable fumes/smoke, which are pollutants and pose a health risk to individuals who inhale them.
- ABS is not biodegradable and, if not recycled, can produce hazardous trash.
- ABS degrades quickly when exposed to the elements or in high-friction settings.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Is ABS Plastic Toxic?
ABS is thought to be non-toxic, however, when burned, it could generate potentially dangerous vapors. When working with ABS goods, it is critical to use them in well-ventilated spaces and to follow all safety precautions.
What is the difference between ABS and PVC?
ABS and polyvinyl chloride (PVC) are both thermoplastics, however they differ significantly. ABS has stronger impact resistance and is more durable, whereas PVC is more flexible and has a lower melting point. The particular requirements of the work at hand will determine which of the two materials is best.
Will hot water damage ABS systems?
ABS pipe can operate at temperatures as high as 140°F (60°C). Furthermore, it absorbs heat slowly and is unaffected by high-temperature water emitted from dishwashers and washing machines.
Video on ABS Plastic
References
- https://europlas.com.vn/en-US/blog-1/abs-material-properties-and-common-applications
- https://www.madearia.com/blog/the-manufacturing-guide-of-plastic-abs-materials/
- https://www.tralert.com/en/lighting-terms/abs-material/
- https://adrecoplastics.co.uk/abs-plastic-properties/
- https://www.xometry.com/resources/materials/abs-plastic/
- https://www.protolabs.com/materials/abs/
- https://www.sharrettsplating.com/blog/what-is-abs-plastic/

