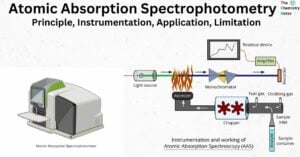
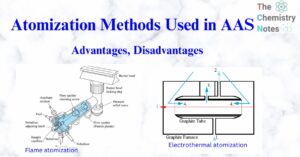
Microspectrophotometer: Working, Components, Advantages, Application
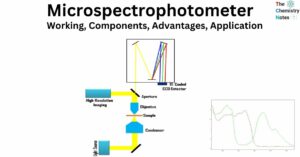
The microspectrophotometer is a device that combines the optical capabilities of a microscope and a spectrophotometer. Microspectroscopy instruments are utilized for the purpose of measuring molecular spectra of samples that are microscopic in nature or microscopic features of samples that … Read more