EDTA: Titration, Types, Advantages, Disadvantages
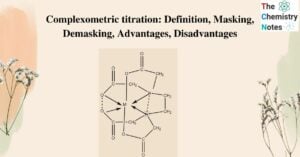
EDTA (Ethylene Diamine Tetraacetic Acid) is an organic reagent that is frequently used in the complexometric titration. It is a chelating ligand with two nitrogen and four carboxylic acids that coordinates with metal ions. Structure of EDTA EDTA is made … Read more