Heavy Water (Deuterium Oxide): Properties, Uses, Reactions
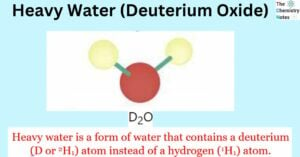
Heavy water, scientifically called deuterium oxide, is a variant of water wherein the regular hydrogen atoms are replaced by heavy hydrogen, commonly known as deuterium. Alternatively, it can be expressed as 2H2O or D2O. Deuterium exhibits distinct characteristics compared to … Read more