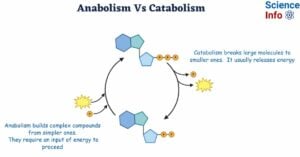
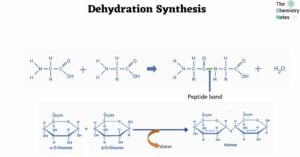
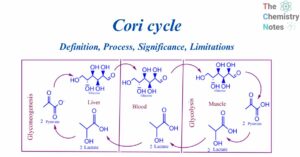
Hydropathy Plots: Definition, Figure, Importance
Hydropathy plot, a plot that is used for the determination of the hydrophilicity and hydrophobicity of protein’s amino acid. It is employed to describe or pinpoint a protein’s potential structure or domains. The plot’s y-axis represents the degree of hydrophilicity … Read more