Iron (Fe): Metallic Element Properties, Uses, Toxicity
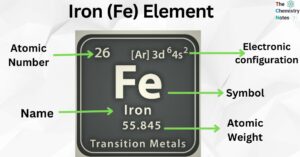
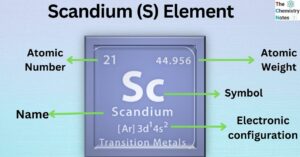
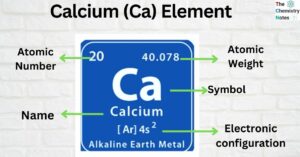
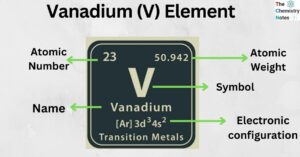
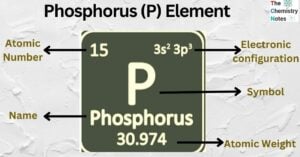
Iron is the metallic element with the atomic number 26 and is represented by the symbol ‘Fe’ in the periodic table. It is classified as a transition metal and belongs to the d-block of group 8 (VIII) of the periodic … Read more