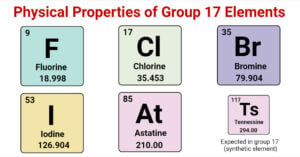
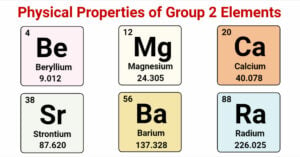
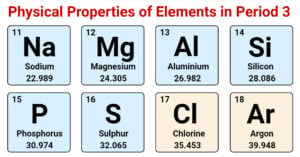
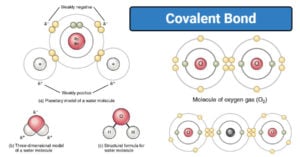
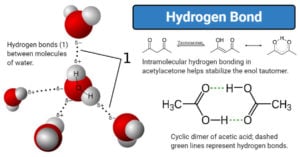
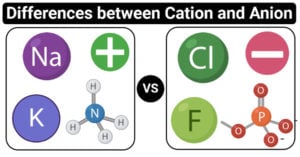
Physical Properties of Group 17 Elements of Periodic Table
Group 17 of the periodic table is named Halogens as they all produce sodium salts with similar properties. In Greek, halo means salt, and genes mean generating, so salt-producing is a collective meaning of the term. Halogens are also known … Read more