The functional groups are the reactive group present in compounds that determine the chemical properties of these compounds. Eg: -OH, -F, -CHO, -COOH.
Interesting Science Videos
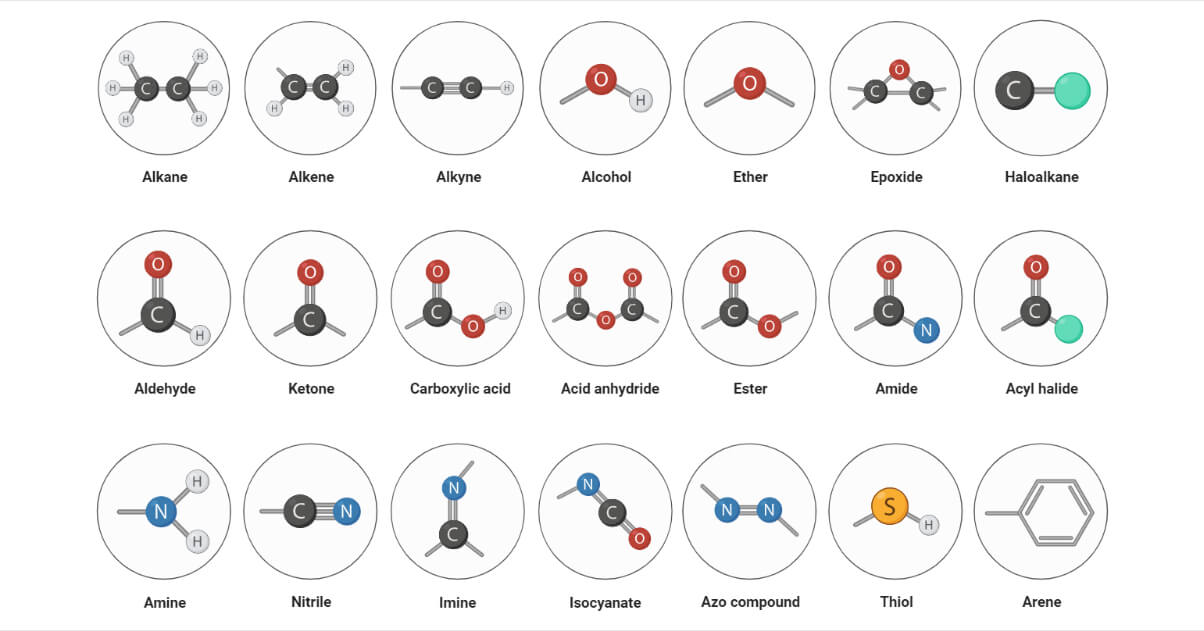
Types of Functional Groups
Hydrocarbons
This includes alkane, alkene, alkyne, and benzene derivatives. They are typically denoted by the symbol -R. Hydrocarbons are made up of carbon and hydrogen that are linked together by various types of bonds, such as single, double, and triple bonds that determine their reactivity. E.g., alkane, alkene, alkyne.
Haloalkanes
Haloalkanes are alkyl halides that consist of a carbon-halogen bond. The strength and stability of the carbon-halogen bond determine the reactivity of these compounds. E.g., chloroalkane, bromoalkane, iodoalkane
Nitrogen containing functional group
These are the functional groups containing carbon-nitrogen bonds. They typically contain amines and amides. E.g., amides, amines, imines, azo compounds
Oxygen containing functional groups
They consist of the carbon-oxygen bond. The properties of compounds containing carbon-oxygen bonds are determined by the hybridization of the carbon-oxygen bond. E.g., alcohols, ketones, aldehydes, peroxides.
Sulphur containing functional groups
This type of functional group consists of the carbon-oxygen bond. Sulfur-containing compounds have distinct chemistry due to their ability to form more bonds than oxygen. E.g., thiols, thials, disulfur.
Phosphorous containing functional groups
Phosphorus-containing compounds have distinct chemistry due to their ability to form more bonds than nitrogen. Many phosphorous-containing functional groups consist of carbon-phosphorous and phosphorous-oxygen bonds. Phosphate diphosphate and triphosphate groups are linked to carbon via phosphate ester linkages in a variety of organic compounds. E.g., phosphine, phosphate group.
List of 35 different functional groups
| S.N. | Functional group | Structure | Prefix | Suffix | Examples |
| 1. | Carboxylic group | 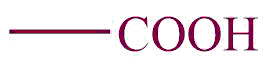 | carboxy | -oic acid | Ethanoic acid(CH3COOH) |
| 2. | Acid Anhydride |  | — | -oic anhydride | Ethanoic anhydride (CH3COOCOCH3) |
| 3. | Carboxylic ester | 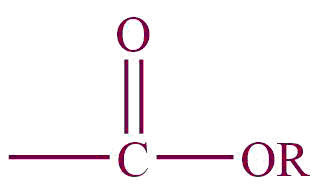 | alkoxycarbonyl | -carboxylate | Methylethanoate (CH3COOCH3) |
| 4. | Amide | 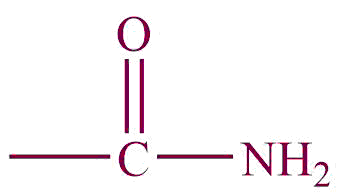 | amide | -carbomyl | Ethanamide (CH3CONH2) |
| 5. | Nitrile |  | cyano | -nitrile | Ethane nitrile(CH3CN) |
| 6. | Aldehyde | 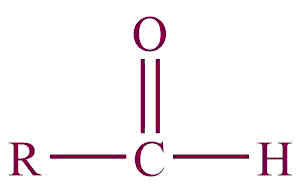 | oxo or formyl | -al, -carbaldehyde | Propanal (C2H5CHO) |
| 7. | Ketone | 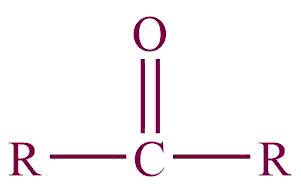 | oxo | -one | Propanone (CH3COCH3) |
| 8. | Alcohol | 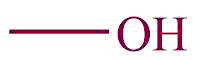 | hydroxy | -ol | Butanol (C4H9OH) |
| 9. | Amine | 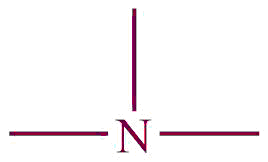 | amino | -amine | Methyl amine (CH3NH2) |
| 10. | Alkene | 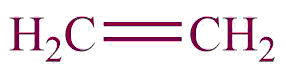 | enyl | -ene | Propene(C3H6) |
| 11. | Alkyne | 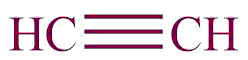 | ynyl | -yne | Propyne (C3H4) |
| 12. | Alkyl |  | yl | -ane | Ethane (C2H6) |
| 13. | Alkyl halide |  | halo(fluro, chloro, bromo, iodo) | – alkyl halide | Chloropropane(C3H7Cl) |
| 14. | Ether | 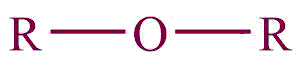 | oxy | ether | Dimethyl ether (CH3OCH3) |
| 15. | Sulphide |  | alkylthio | sulfide | Dimethyl sulfide (CH3SCH3) |
| 16. | Nitro | 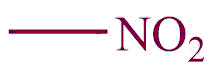 | nitro | – | Nitromethane (CH3NO2) |
| 17. | Benzene | 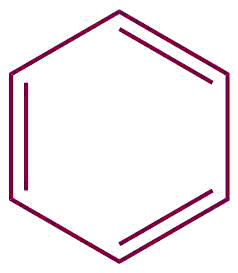 | phenyl | benzene | Ethylbenzene (C6H5C2H5) |
| 18. | Disulphide |  | substituent disalfanyl | -disulfide | Dimethyl disulfide (CH3-S-S-CH3) |
| 19. | Thiol | 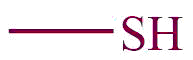 | mercapto | -thiol | Propane-1-thiol (C3H7SH) |
| 20. | Isocyano | 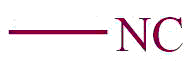 | isocyano | isonitrile | Methyl isonitrile (CH3NC) |
| 21. | Cyanate |  | cyanate | – | |
| 22. | Isocyanate | 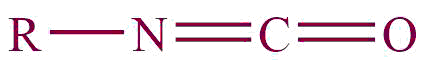 | isocyante | – | Methyl isocyanate (CH3NCO) |
| 23. | Peroxide |  | (R)-peroxy | peroxide | Dimethyl peroxide(C2H6O2) |
| 24. | Hydroperoxy | 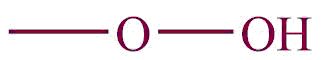 | hydroperoxy | hydroperoxide | Methyl peroxide (CH4O2) |
| 25. | Alcoholates, Phenolates | 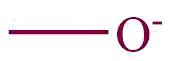 | oxido | | Glyoxylic acid methyl ester methyl alcoholate (C4H7O4–) |
| 26. | Sulphonates | 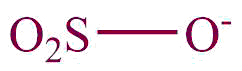 | sulfonato | -sulfonate | Naphthalene-1-sulphonate (C10H7O3S) |
| 27. | Sulfonic acid |  | sulfo | -sulfonic acid | Benzene sulfonic acid (C6H6O3S) |
| 28. | epoxide | 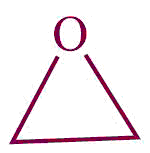 | epoxy | -ene oxide | Propylene oxide (C3H6O) |
| 29. | azo | 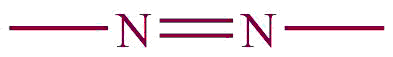 | azo | – | Azobenzene (C12H10O2) |
| 30. | Sulfoxide | 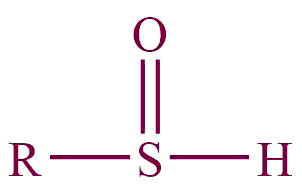 | sulfinyl | -sulphoxide | Dimethyl sulphoxide (CH3SOCH3) |
| 31. | Sulfone | 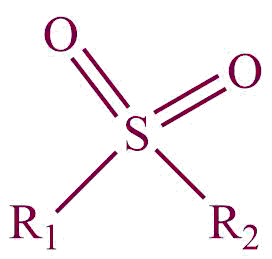 | sulfonyl | -sulfone | Dimethyl sulfone (CH3SO2CH3) |
| 32. | Sulfinic acid | 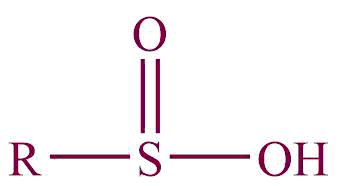 | sulfino | -sulfinic acid | Propanesulfinic acid (C3H7SO2H) |
| 33. | Thial | 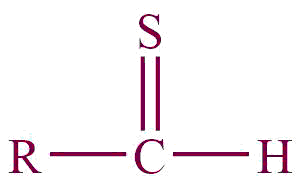 | thial | | Methanethial (CH3SH) |
| 34. | Thiocyante |  | thiocyanate | | Ethyl thiocyanate (C2H5-S-CN) |
| 35. | phosphine | 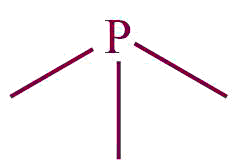 | phosphanyl | -phosphane | (C3H7-PH2) |
References
- https://chem.libretexts.org/Courses/Sacramento_City_College/SCC%3A_CHEM_330_-Adventures_in_Chemistry(Alviar-Agnew)/09%3A_Organic_Chemistry/9.09%3A_Nitrogen-Containing_Compounds-_Amines_and_Amides
- https://www.britannica.com/science/functional-group
- https://kpu.pressbooks.pub/organicchemistry/chapter/2-4-naming-of-organic-compounds-with-functional-groups/
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Functional_group
- https://byjus.com/chemistry/functional-groups/
- https://www.vedantu.com/chemistry/nomenclature-functional-groups
- https://www.compoundchem.com/2020/02/21/functional-groups/
