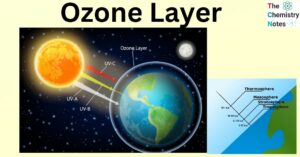
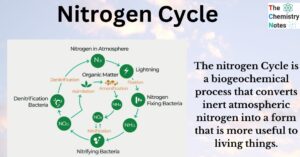
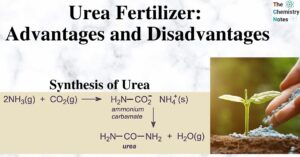
Ecotoxicology: Toxic Elements, Effects, Routes of Exposure
Ecotoxicology combines elements of ecology, toxicology, physiology, analytical chemistry, molecular biology, and mathematics. Ecotoxicology studies how pollutants, such as pesticides, affect people, populations, the environment, and ecosystems. Ecosystems are made … Read more