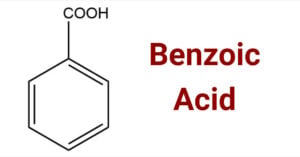
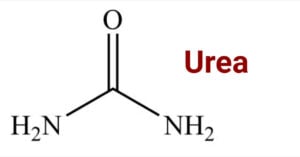
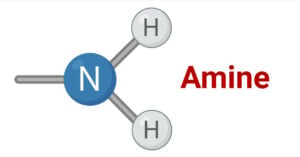
Benzaldehyde- Definition, Preparation, Properties, Uses
Benzaldehyde is an aromatic aldehyde in which the -CHO group is directly bonded to the aromatic ring. It is a compound with a molecular formula C7H6O that has several industrial applications, including the preparation of dyes, cosmetic products, and flavoring … Read more