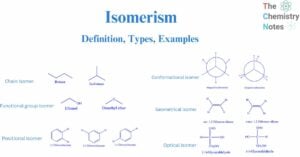
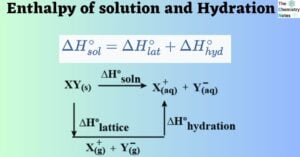
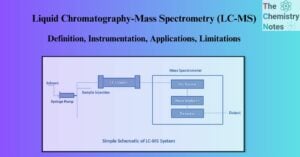
Potable Water: Sources, Purification Methods, Water Treatment
The term “potable water” refers to water that is safe for human consumption, which means that it can either be consumed directly or utilized in the preparation of food. The word suggests that the water is fit for human consumption … Read more