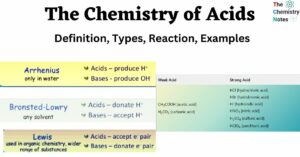
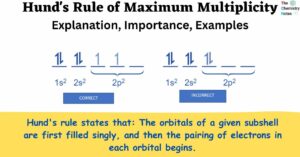
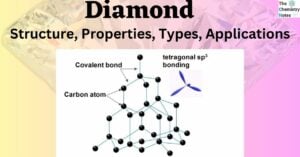
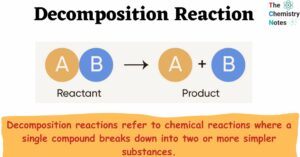
The Chemistry of Acids: Definition, Types, Reaction, Examples
Acids can be either organic or inorganic, and they can also be particularly strong or weak. They frequently arise on their own. As an illustration, hydrochloric acid can be discovered in the stomachs of mammals, including humans. Citric acid, present … Read more