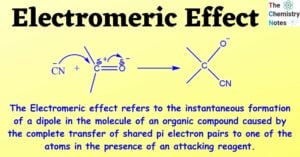
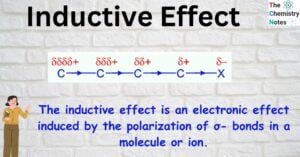
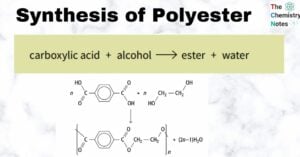
Acyl chloride: Nomenclature, Preparation, Properties, Uses
Acyl chloride is an important derivative of carboxylic acid. It has an sp 2 hybridized carbonyl group with an O atom connected to a C atom through a double bond in a planar form with bond angles of about 120o. It … Read more