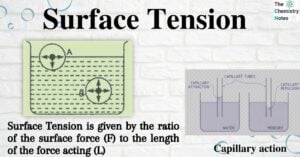
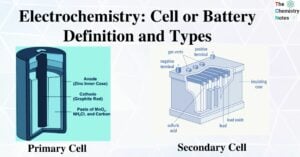
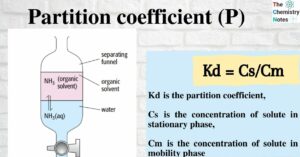
Electrolytic Cell: Definition, Principle, Components, Application, Examples
An electrolytic cell is crucial to the functions of daily life; they charge many electronic devices, such as phones and electric cars. Electrolytic cells use an electric current to drive a chemical reaction backward, adding potential energy to a system. … Read more