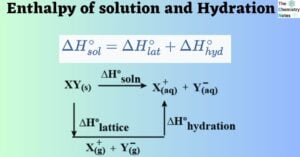
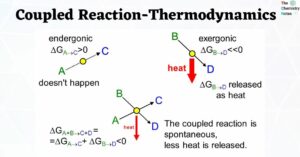
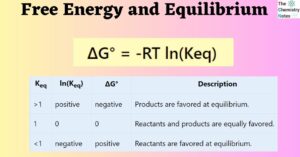
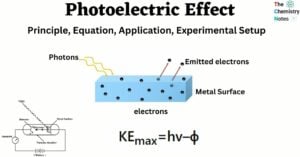
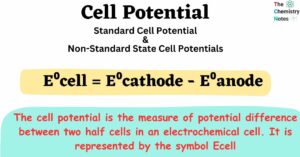
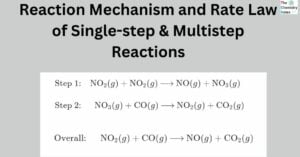
Enthalpy of solution and Hydration
An ionic solid dissolves in water, which causes the crystal lattice to disintegrate and the ions to disperse. Overcoming the attractive forces between ions necessitates a significant amount of energy. Enthalpy of Solution The enthalpy of solution refers to the … Read more