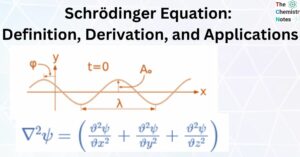
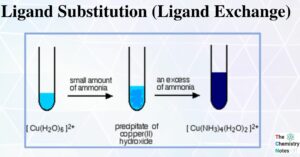
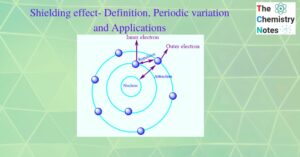
Lanthanide Contraction: Definition, Causes, and Consequences
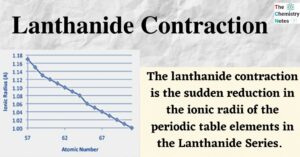
Lanthanide Contraction is an intriguing exception to examine in Chemistry. It is occasionally referred to as the Lanthanoid Contraction. It is applicable to the elements in the Periodic Table’s Lanthanide Series. The atomic numbers of the lanthanide series vary from 57 … Read more