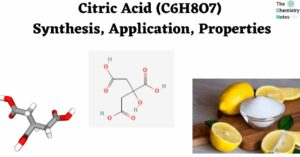
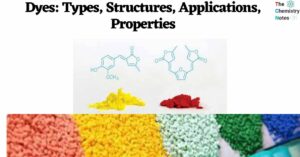
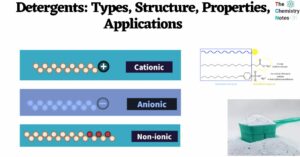
Alum: Properties, Types, Amazing Applications
Alum is an inorganic compound consisting of water molecules, aluminum, other metals besides aluminum, and sulfates. Alum, in its hydrated state, is classified as a double salt. There are various forms of alum, including Potash Alum, Soda Alum, Ammonium Alum, … Read more