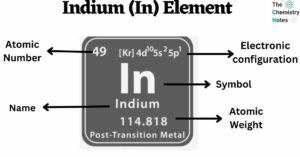
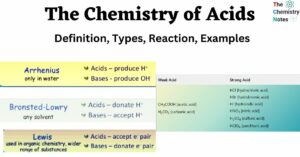
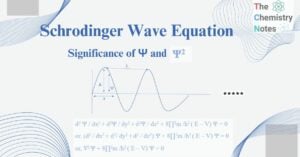
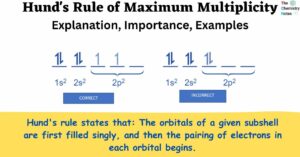
Azo Compounds: Preparation, Types, Properties, Applications, Examples
Azo compounds are the compounds of both natural and manufactured chemicals that contain at least one azo group (N=N) in their structure. The atomic groups connected to the nitrogen atoms might be of any organic class, but the commercially relevant azo … Read more