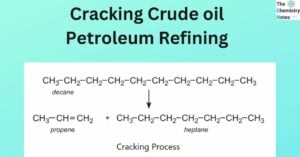
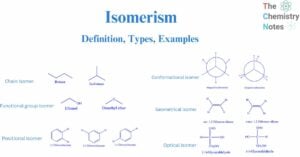
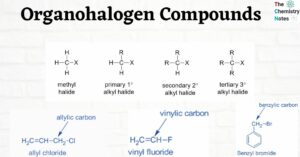
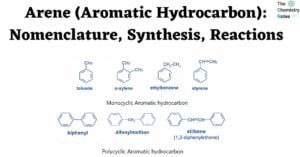
Tautomerism: Condition, Features, Types,
Tautomerism is the existence of two or more chemical compounds that are easily interconvertible, frequently by simply exchanging one hydrogen atom for another between two other atoms, to either of which it forms a covalent connection. Tautomerism refers to the rapid … Read more