Differential and Integrated Rate Equation
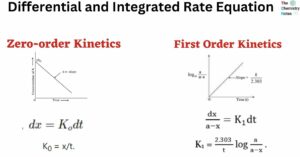
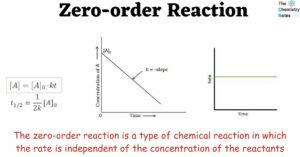
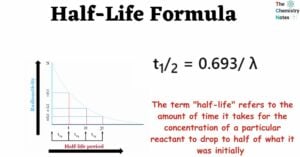
Differential and Integrated Rate Equation of Zero Order Kinetics A reaction is considered to be of zero order if its rate is independent of the concentration of the reactants. Let us consider a general zero-order reaction. Initially concentration At time … Read more